Appendix D — Division B
Fire-Performance Ratings
Section D-1. General
D-1.1. Introduction
D-1.1.1. Scope

D-1.1.2. Referenced Documents
| Table D-1.1.2. Documents Referenced in Appendix D Fire-Performance Ratings Forming part of Sentence (1) | |||
| Issuing Agency | Document Number(1) | Title of Document(2) | Reference |
| ANSI | A208.1-2009 | Particleboard | Table D-3.1.1.A. |
 ASTM ASTM |
C 330/C 330M-09 | Lightweight Aggregates for Structural Concrete | D-1.4.3.(2) |
 ASTM ASTM |
C 1396/C 1396M-11 | Gypsum Board | D-1.5.1. Table D-3.1.1.A.  |
| CCBFC | NRCC 30629 | Supplement to the National Building Code of Canada 1990 | D-6.2. D-6.3. D-6.4. |
| CGSB | 4-GP-36M-1978 | Carpet Underlay, Fiber Type | Table D-3.1.1.B. |
| CGSB | CAN/CGSB-4.129-97 | Carpets for Commercial Use | Table D-3.1.1.B. |
| CGSB | CAN/CGSB-11.3-M87 | Hardboard | Table D-3.1.1.A. |
| CGSB | CAN/CGSB-92.2-M90 | Trowel or Spray Applied Acoustical Material | D-2.3.4.(5) |
| CSA | A23.1-09/A23.2-09 | Concrete Materials and Methods of Concrete Construction/Test Methods and Standard Practices for Concrete | D-1.4.3.(1) |
| CSA | CAN/CSA-A23.3-04 | Design of Concrete Structures | D-2.1.5.(2) D-2.6.6.(1) Table D-2.6.6.B. D-2.8.2.(1) Table D-2.8.2. |
| CSA | A82.5-M1978 | Structural Clay Non-Load-Bearing Tile | Table D-2.6.1.A. |
| CSA | A82.22-M1977 | Gypsum Plasters | Table D-3.1.1.A. |
| CSA | CAN/CSA-A82.27-M91 | Gypsum Board | D-1.5.1. Table D-3.1.1.A. |
| CSA | A82.30-M1980 | Interior Furring, Lathing and Gypsum Plastering | D-1.7.2.(1) D-2.3.9.(1) Table D-2.5.1. |
| CSA | A82.31-M1980 | Gypsum Board Application | D-2.3.9.(1) D-2.3.9.(6) |
| CSA | CAN/CSA-A165.1-04 | Concrete Block Masonry Units | Table D-2.1.1. |
| CSA | O86-09 | Engineering Design in Wood | D-2.11.2.(1) D-2.11.2.(2) |
| CSA | O121-08 | Douglas Fir Plywood | Table D-3.1.1.A. |
| CSA | O141-05 | Softwood Lumber | D-2.3.6.(2) Table D-2.4.1. |
| CSA | O151-09 | Canadian Softwood Plywood | Table D-3.1.1.A. |
| CSA | O153-M1980 | Poplar Plywood | Table D-3.1.1.A. |
| CSA | CAN/CSA-O325-07 | Construction Sheathing | D-3.1.1.A. |
| CSA | O437.0-93 | OSB and Waferboard | Table D-3.1.1.A. |
| CSA | S16-09 | Design of Steel Structures | D-2.6.6.(1) D-2.6.6.(3) Table D-2.6.6.B. |
 NFPA NFPA |
80-2010 | Fire Doors and Other Opening Protectives | D-5.2.1.(1) D-5.2.1.(2)  |
| ULC | CAN/ULC-S101-07 | Fire Endurance Tests of Building Construction and Materials | D-1.1.1.(4) D-1.12.1. D-2.3.2. |
 ULC ULC |
CAN/ULC-S102-10 | Test for Surface Burning Characteristics of Building Materials and Assemblies | D-1.1.1.(5) |
 ULC ULC |
CAN/ULC-S102.2-10 | Test for Surface Burning Characteristics of Flooring, Floor Coverings, and Miscellaneous Materials and Assemblies | D-1.1.1.(5) Table D-3.1.1.B.  |
| ULC | CAN/ULC-S114-05 | Test for Determination of Non-Combustibility in Building Materials | D-1.1.1.(6) D-4.1.1.(1) D-4.2.1. |
| ULC | ULC-S505-1974 | Fusible Links for Fire Protection Service | D-5.3.2. |
| ULC | CAN/ULC-S702-09 | Mineral Fibre Thermal Insulation for Buildings | Table D-2.3.4.A. Table D-2.3.4.D. D-2.3.5.(2) D-2.3.5.(4) Table D-2.6.1.E. D-6.4. |
 ULC ULC |
CAN/ULC-S703-09 | Cellulose Fibre Insulation (CFI) for Buildings | D-2.3.4.(5) |
 ULC ULC |
CAN/ULC-S706-09 | Standard for Wood Fibre Insulating Boards for Buildings | Table D-3.1.1.A. |

D-1.1.3. Applicability of Ratings
D-1.1.4. Higher Ratings
D-1.1.5. Additional Information on Fire Rated Assemblies
D-1.2. Interpretation of Test Results
D-1.2.1. Limitations

D-1.3. Concrete
D-1.3.1. Aggregates in Concrete
D-1.4. Types of Concrete
D-1.4.1. Description
D-1.4.2. Determination of Ratings
D-1.4.3. Description of Aggregates
 ASTM C 330/C 330M, “Lightweight Aggregates for Structural Concrete.”
ASTM C 330/C 330M, “Lightweight Aggregates for Structural Concrete.”

D-1.5. Gypsum Wallboard
D-1.5.1. Types of Wallboard
D-1.6. Equivalent Thickness
D-1.6.1. Method of Calculating
- ta for s less than or equal to 2 t,
- t + (4 t/s - 1)(ta - t) for s less than 4 t and greater than 2 t, and
- t for s greater than or equal to 4 t
D-1.7. Contribution of Plaster or Gypsum Wallboard Finish to Fire Resistance of Masonry or Concrete
D-1.7.1. Determination of Contribution
| Table D-1.7.1. Multiplying Factors for Masonry or Concrete Construction Forming part of Sentence (1) | ||||
| Type of Surface Protection | Type of Masonry or Concrete | |||
| Solid Clay Brick, Unit Masonry and Monolithic Concrete, Type N or S |
Cored Clay Brick, Clay Tile, Monolithic Concrete, Type L40S and Unit Masonry, Type L120S |
Concrete Unit Masonry, Type L1 or L220S and Monolithic Concrete, Type L |
Concrete Unit Masonry, Type L2 |
|
| Portland cement-sand plaster or lime sand plaster | 1 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.50 |
| Gypsum-sand plaster, wood fibred gypsum plaster or gypsum wallboard | 1.25 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Vermiculite or perlite aggregate plaster | 1.75 | 1.5 | 1.25 | 1.25 |
D-1.7.2. Plaster
D-1.7.3. Attachment of Wallboard and Lath
D-1.7.4. Sample Calculations
- The minimum equivalent thickness of Type S monolithic concrete needed to give a 3 h fire-resistance rating = 158 mm (Table D-2.1.1.).
- Since the gypsum-sand plaster finish is applied on metal lath, D-1.7.1.(5) does not apply. Therefore, the contribution to the equivalent thickness of the wall of 20 mm gypsum-sand plaster on each face of the concrete is 20 × 1.25 = 25 mm (see D-1.7.1.(1) to (4)).
- The total contribution of the plaster finishes is 2 × 25 = 50 mm.
- The minimum equivalent thickness of concrete required is 158 mm - 50 mm = 108 mm.
- From Table D-2.1.1., the 108 mm equivalent thickness of monolithic concrete gives a contribution of less than 1.5 h. This is less than half the rating of the assembly so that the conditions in D-1.7.1.(2) are not met. Thus the equivalent thickness of monolithic concrete must be increased to 112 mm to give 1.5 h contribution.
- The total equivalent thickness of the plaster finishes can then be reduced to 158 mm - 112 mm = 46 mm.
- The total actual thickness of the plaster finishes required is therefore 46 mm ÷ 1.25 = 37 mm (D-1.7.1.(1) to (4)) or 18.5 mm on each face.
- Since the thickness of the plaster finish on each face exceeds 16 mm, metal lath is still required (D-1.7.2.(4)).
- Since this wall is symmetrical with plaster on both faces, the contribution to fire resistance of the plaster finish on either face is limited to one-quarter of the wall rating by virtue of D-1.7.1.(2). Under these circumstances, the conditions in D-1.7.1.(4) are automatically met.
- Since gypsum wallboard is used, D-1.7.1.(5) applies. The 12.7 mm gypsum wallboard finish on the fire-exposed side is, therefore, assigned 25 min by using Table D-2.3.4.A.
- The fire resistance required of the balance of the assembly is 120 min - 25 min = 95 min.
- Interpolating between 1.5 h and 2 h in Table D-2.1.1. for 95 min fire resistance, the equivalent thickness for hollow masonry units required is 95 mm + (18 mm × 5/30) = 95 mm + 3 mm = 98 mm.
- The contribution to the equivalent thickness of the wall of the 12.7 mm gypsum wallboard finish on the non-fire-exposed side using Table D-1.7.1. = 12.7 × 1.25 = 16 mm.
- Equivalent thickness required of concrete masonry unit = 98 - 16 = 82 mm.
- The fire-resistance rating of a concrete masonry wall having an equivalent thickness of 82 mm = 1 h for 73 mm + (9 mm × 30/22) = 1 h 12 min.
- According to Table D-2.1.1., the minimum equivalent thickness for Type L220S concrete masonry units needed to achieve a 2 h rating is 94 mm.
- Since gypsum wallboard is not used on the fire-exposed side, D-1.7.1.(5) does not apply. The contribution to the equivalent thickness of the wall by the 15.9 mm Type X gypsum wallboard finish applied on the non-fire-exposed side is 15.9 × 1 ≈ 16 mm (see D-1.7.1.(1) and Table D-1.7.1.).
- Therefore, the equivalent thickness required of the concrete masonry unit is 94 - 16 = 78 mm.
- The contribution to fire resistance of a 78 mm L 220S concrete hollow masonry unit is 85 min. The contribution of the Type X gypsum wallboard finish is 120 - 85 = 35 min, which does not exceed half the 85 min contribution of the masonry unit or 42.5 min, so that the conditions in D-1.7.1.(4) are met.
- The rating of the wall (120 min) is less than twice the contribution of the masonry unit (170 min) so that the conditions in D-1.7.1.(2) are also met.
D-1.8. Tests on Floors and Roofs
D-1.8.1. Exposure to Fire
D-1.9. Moisture Content
D-1.9.1. Effect of Moisture
D-1.10. Permanence and Durability
D-1.10.1. Test Conditions
D-1.11. Steel Structural Members
D-1.11.1. Thermal Protection
D-1.12. Restraint Effects
D-1.12.1. Effect on Fire-Resistance Ratings
Section D-2. Fire-Resistance Ratings
D-2.1. Masonry and Concrete Walls
D-2.1.1. Minimum Equivalent Thickness for Fire-Resistance Rating
| Table D-2.1.1. Minimum Equivalent Thicknesses(1) of Unit Masonry and Monolithic Concrete Walls Loadbearing and Non-Loadbearing, mm Forming part of Article D-2.1.1. | |||||||
| Type of Wall | Fire-Resistance Rating | ||||||
| 30 min | 45 min | 1 h | 1.5 h | 2 h | 3 h | 4 h | |
| Solid brick units (80% solid and over), actual overall thickness | 63 | 76 | 90 | 108 | 128 | 152 | 178 |
| Cored brick units and hollow tile units (less than 80% solid), equivalent thickness | 50 | 60 | 72 | 86 | 102 | 122 | 142 |
| Solid and hollow concrete masonry units, equivalent thickness | |||||||
| Type S or N concrete(2) | 44 | 59 | 73 | 95 | 113 | 142 | 167 |
| Type L120S concrete | 42 | 54 | 66 | 87 | 102 | 129 | 152 |
| Type L1 concrete | 42 | 54 | 64 | 82 | 97 | 122 | 143 |
| Type L220S concrete | 42 | 54 | 64 | 81 | 94 | 116 | 134 |
| Type L2 concrete | 42 | 54 | 63 | 79 | 91 | 111 | 127 |
| Monolithic concrete and concrete panels, equivalent thickness | |||||||
| Type S concrete | 60 | 77 | 90 | 112 | 130 | 158 | 180 |
| Type N concrete | 59 | 74 | 87 | 108 | 124 | 150 | 171 |
| Type L40S or Type L concrete | 49 | 62 | 72 | 89 | 103 | 124 | 140 |
| Notes to Table D-2.1.1.: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | See definition of equivalent thickness in Subsection D-1.6. |
| (2) | Hollow concrete masonry units made with Type S or N concrete shall have a minimum compressive strength of 15 MPa based on net area, as defined in CAN/CSA-A165.1, “Concrete Block Masonry Units.” |
D-2.1.2. Applicability of Ratings
D-2.1.3. Framed Beams and Joists
D-2.1.4. Credit for Plaster Thickness
D-2.1.5. Walls Exposed to Fire on Both Sides
- its equivalent thickness is not less than 200 mm,
- its aspect ratio (width/thickness) is not less than 4.0,
- the minimum thickness of concrete cover over the steel reinforcement specified in Clause (d) is not less than 50 mm,
- each face of the wall is reinforced with both vertical and horizontal steel reinforcement in conformance with either Clause 10 or Clause 14 of CAN/CSA-A23.3, “Design of Concrete Structures,”
- the structural design of the wall is governed by the minimum eccentricity (15 + 0.03h) specified in Clause 10.15.3.1 of CAN/CSA-A23.3, “Design of Concrete Structures,” and
- the effective length of the wall,
klu, is not more than 3.7 m
wherek= effective length factor obtained from CAN/CSA-A23.3, “Design of Concrete Structures,”lu= unsupported length of the wall in metres.
D-2.2. Reinforced and Prestressed Concrete Floor and Roof Slabs
D-2.2.1. Assignment of Rating
| Table D-2.2.1.A. Minimum Thickness of Reinforced and Prestressed Concrete Floor or Roof Slabs, mm Forming part of Sentence (1) | |||||||
| Type of Concrete | Fire-Resistance Rating | ||||||
| 30 min | 45 min | 1 h | 1.5 h | 2 h | 3 h | 4 h | |
| Type S concrete | 60 | 77 | 90 | 112 | 130 | 158 | 180 |
| Type N concrete | 59 | 74 | 87 | 108 | 124 | 150 | 171 |
| Type L40S or Type L concrete | 49 | 62 | 72 | 89 | 103 | 124 | 140 |
| Table D-2.2.1.B. Minimum Concrete Cover over Reinforcement in Concrete Slabs, mm Forming part of Sentence (2) | |||||||
| Type of Concrete | Fire-Resistance Rating | ||||||
| 30 min | 45 min | 1 h | 1.5 h | 2 h | 3 h | 4 h | |
| Type S, N, L40S or L concrete | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 25 | 32 | 39 |
| Prestressed concrete slabs Type S, N, L40S or L concrete | 20 | 25 | 25 | 32 | 39 | 50 | 64 |
D-2.2.2. Floors with Hollow Units
D-2.2.3. Composite Slabs
- when the base layer consists of Type S or N
concrete,
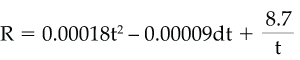
- when the base layer consists of Type L40S
or L concrete,
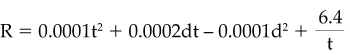 whereR= fire resistance of slab, h,t= total thickness of slab, mm, andd= thickness of base layer, mm.
whereR= fire resistance of slab, h,t= total thickness of slab, mm, andd= thickness of base layer, mm.
| Table D-2.2.3.A. Multiplying Factors for Equivalent Thickness Forming part of Sentence (2) | ||
| Top Course Material | Base Slab Normal Density
Concrete (Type S or N) |
Base Slab Low Density
Concrete (Type L40S or L) |
| Gypsum wallboard | 3 | 2.25 |
|
Cellular concrete (mass density 400 – 560 kg/m3 ) |
2 | 1.50 |
| Vermiculite and perlite concrete (mass density 560 kg/m3 or less) | 1.75 | 1.50 |
| Portland cement with sand aggregate | 1 | 0.75 |
| Terrazzo | 1 | 0.75 |
| Table D-2.2.3.B. Minimum Concrete Cover under Bottom Reinforcement in Composite Concrete Slabs, mm Forming part of Sentence (3) | |||||||
| Base Slab Concrete Type | Fire-Resistance Rating | ||||||
| 30 min | 45 min | 1 h | 1.5 h | 2 h | 3 h | 4 h | |
| Reinforced concrete | |||||||
| Type S, N, L40S or L | 15 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 55 |
| Prestressed concrete | |||||||
| Type S | 20 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 65 | 75 |
| Type N | 20 | 20 | 25 | 35 | 45 | 60 | 70 |
| Type L40S or L | 20 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
D-2.2.4. Contribution of Plaster Finish
D-2.2.5. Concrete Cover
D-2.2.6. Minimum Dimensions for Cover
D-2.3. Wood and Steel Framed Walls, Floors and Roofs
D-2.3.1. Maximum Fire-Resistance Rating
D-2.3.2. Loadbearing Conditions
D-2.3.3. Limitations of Component Additive Method
(See D-6., Background Information.)D-2.3.4. Method of Calculation
| Table D-2.3.4.A. Time Assigned to Wallboard Membranes on Fire-Exposed Side Forming part of Article D-2.3.4. | |
| Description of Finish | Time, min |
| 11.0 mm Douglas Fir plywood phenolic bonded |
10(1) |
| 14.0 mm Douglas Fir plywood phenolic bonded |
15(1) |
| 12.7 mm Type X gypsum wallboard | 25 |
| 15.9 mm Type X gypsum wallboard | 40 |
| Double 12.7 mm Type X gypsum wallboard |
80(2) |
| Notes to Table D-2.3.4.A.: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | Non-loadbearing walls only, stud cavities filled with mineral wool conforming to CAN/ULC-S702, “Mineral Fibre Thermal Insulation for Buildings,” and having a mass of not less than 2 kg/m2, with no additional credit for insulation according to Table D-2.3.4.D. |
| (2) | Applies to non-loadbearing steel framed walls only. |
| Table D-2.3.4.B. Time Assigned for Contribution of Lath and Plaster Protection on Fire-Exposed Side, min(1) Forming part of Article D-2.3.4. | ||||
| Type of Lath | Plaster Thickness, mm | Type of Plaster Finish | ||
|
Portland Cement and Sand(2) or Lime and Sand |
Gypsum and Sand or Gypsum Wood Fibred | Gypsum and Perlite or Gypsum and Vermiculite | ||
| 9.5 mm gypsum | 13 | — | 35 | 55 |
| 16 | — | 40 | 65 | |
| 19 | — | 50 |
80(1) |
|
| Metal | 19 | 20 | 50 |
80(1) |
| 23 | 25 | 65 |
80(1) |
|
| 26 | 30 | 80 |
80(1) |
|
| Notes to Table D-2.3.4.B.: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | Values shown for these membranes have been limited to 80 min because the fire-resistance ratings of framed assemblies derived from these Tables shall not exceed 1.5 h. |
| (2) | For mixture of Portland cement-sand plaster, see D-1.7.2.(2). |
| Table D-2.3.4.C. Time Assigned for Contribution of Wood or Light Steel Frame Forming part of Article D-2.3.4. | |
| Description of Frame | Time Assigned to Frame, min |
|
Wood studs 400 mm o.c. maximum |
20 |
|
Wood studs 600 mm o.c. maximum |
15 |
|
Steel studs 400 mm o.c. maximum |
10 |
|
Wood floor and wood roof joists 400 mm o.c. maximum |
10 |
|
Open web steel joist floors and roofs with ceiling supports 400 mm o.c. maximum |
10 |
|
Wood roof and wood floor truss assemblies 600 mm o.c. maximum |
5 |
| Table D-2.3.4.D. Time Assigned for Additional Protection Forming part of Article D-2.3.4. | |
| Description of Additional Protection | Time Assigned, min |
|
Add to the fire-resistance rating of wood stud walls, sheathed with gypsum wallboard or lath and plaster, if the spaces between the studs are filled with preformed insulation of rock or slag fibres conforming to CAN/ULC-S702, “Mineral Fibre Thermal Insulation for Buildings,” and with a mass of not less than 1.22 kg/m2 of wall surface(1) |
15 |
|
Add to the fire-resistance rating of non-loadbearing wood stud walls, sheathed with gypsum wallboard or lath and plaster, if the spaces between the studs are filled with preformed insulation of glass fibres conforming to CAN/ULC-S702, “Mineral Fibre Thermal Insulation for Buildings,” and having a mass of not less than 0.6 kg/m2 of wall surface |
5 |
|
Add to the fire-resistance rating of plaster on gypsum lath ceilings if 0.76 mm diam wire mesh with 25 mm by 25 mm openings or 1.57 mm diam diagonal wire reinforcing at 250 mm o.c. is placed between lath and plaster |
30 |
|
Add to the fire-resistance rating of plaster on gypsum lath ceilings if 76 mm wide metal lath strips are placed over joints between lath and plaster |
10 |
|
Add to the fire-resistance rating of plaster on 9.5 mm thick gypsum lath ceilings (Table D-2.3.4.B.) if supports for lath are 300 mm o.c. |
10 |
| Notes to Table D-2.3.4.D.: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | There are no test data to justify the 15 min additional protection for preformed glass fibre insulation. |
D-2.3.5. Considerations for Various Types of Assemblies
| Table D-2.3.5. Flooring or Roofing Membranes for Wood, Cold Formed Steel Members or Open-Web Steel Joists Forming part of Article D-2.3.5. | |||
| Type of Assembly | Structural Members | Subfloor or Roof Deck | Finish Flooring or Roofing |
| Floor | Wood or steel joists and wood trusses |
12.5 mm plywood or |
Hardwood or softwood flooring on building paper |
| Resilient flooring, parquet floor, felted synthetic fibre floor coverings, carpeting, or ceramic tile on 8 mm thick panel-type underlay | |||
| Ceramic tile on 30 mm mortar bed | |||
| Steel joists |
50 mm reinforced
concrete or |
Finish flooring | |
| Roof | Wood or steel joists and wood trusses |
12.5 mm plywood
or |
Finish roofing material with or without insulation |
| Steel joists |
50 mm reinforced concrete or 50 mm concrete on metal lath or formed steel sheet, or 40 mm reinforced gypsum-fibre concrete on 12.7 mm gypsum wallboard |
Finish roofing material with or without insulation | |
- the insulation is preformed of rock, slag or glass fibre conforming to CAN/ULC-S702, “Mineral Fibre Thermal Insulation for Buildings,” and having a mass of not more than 1.1 kg/m2 and is installed adjacent to the bottom edge of the framing member, directly above steel furring channels,
- the gypsum wallboard ceiling membrane is attached to
- wood trusses in conformance with D-2.3.9.(2) by way of steel drywall furring channels spaced not more than 400 mm o.c., and the channels are secured to each bottom truss member with a double strand of 1.2 mm galvanized steel wire, or
- wood joists by way of drywall or resilient steel furring channels spaced not more than 400 mm o.c. in conformance with D-2.3.9.(2) and (3), and
- a steel furring channel is installed midway between each furring channel mentioned in Clause (b) to provide additional support for the insulation.
D-2.3.6. Framing Members
D-2.3.7. Plaster Finish
D-2.3.8. Edge Support for Wallboard
D-2.3.9. Membrane Fastening
| Table D-2.3.9. Minimum Fastener Penetrations for Membrane Protection on Wood Frame, mm Forming part of Article D-2.3.9. | ||||||
| Type of Membrane |
Assigned Contribution of Membrane to Fire Resistance(1), min |
|||||
| 5 – 25 | 30 – 35 | 40 | 50 | 55 – 70 | 80 | |
| Single layer | 20 | 29 | 32 | — | — | — |
| Double layer | 20 | 20 | 20 | 29 | 35 | 44 |
| Gypsum lath | 20 | 20 | 23 | 23 | 29 | 29 |
| Notes to Table D-2.3.9.: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | Assigned contributions of membranes to fire resistance are determined in Tables D-2.3.4.A., D-2.3.4.B. and D-2.3.12. |
D-2.3.10. Ceiling Membrane Openings – Combustible Construction
- the assembly is not required to have a fire-resistance rating in excess of 1 h,
- the area of any openings does not exceed 930 cm2 (see Sentence (2)),
- the aggregate area of openings does not exceed 1% of the ceiling area of the fire compartment,
- the depth of the concealed space above the ceiling is not less than 230 mm,
- no dimension of any opening exceeds 310 mm,
- supports are provided for openings with any dimension exceeding 150 mm where framing members are spaced greater than 400 mm o.c.,
- individual openings are spaced not less than 2 m apart,
- the ducts above the membrane are sheet steel and are supported by steel strapping firmly attached to the framing members, and
- the clearance between the top surface of the membrane and the bottom surface of the ducts is not less than 100 mm.
- a fire stop flap conforming to Subsection D-5.3., or
- thermal protection above the duct consisting of the same materials as used for the ceiling membrane, mechanically fastened to the ductwork and extending 200 mm beyond the opening on all sides (see Article D-2.3.10.A-A).
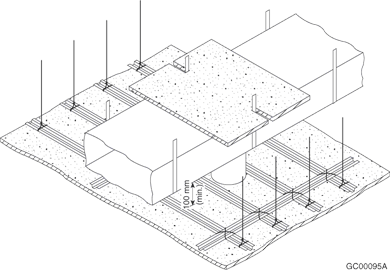
D-2.3.11. Ceiling Membrane Openings – Noncombustible Construction
- the area of any opening does not exceed 930 cm2 (see Sentence (2)),
- the aggregate area of openings does not exceed 2% of the ceiling area of the fire compartment,
- no dimension of any opening exceeds 400 mm,
- individual openings are spaced not less than 2 m apart,
- openings are located not less than 200 mm from major structural members such as beams, columns or joists,
- the ducts above the membrane are sheet steel and are supported by steel strapping firmly attached to the framing members, and
- the clearance between the top surface of the membrane and the bottom surface of the duct is not less than 100 mm.
- a fire stop flap conforming to Subsection D-5.3., or
- thermal protection above the duct consisting of the same materials as used for the ceiling membrane, mechanically fastened to the ductwork and extending 200 mm beyond the opening on all sides (see Article D-2.3.10.A-A).
D-2.3.12. Ceiling Membrane Rating
| Table D-2.3.12. Fire-Resistance Rating for Ceiling Membranes Forming part of Article D-2.3.12. | |
| Description of Membrane | Fire-Resistance Rating, min |
| 15.9 mm Type X gypsum wallboard with ≥ 75 mm mineral wool batt insulation above wallboard | 30 |
|
19 mm gypsum-sand plaster on metal lath |
30 |
| Double 14.0 mm Douglas Fir plywood phenolic bonded | 30 |
|
Double 12.7 mm Type X gypsum wallboard |
45 |
|
25 mm gypsum-sand plaster on metal lath |
45 |
|
Double 15.9 mm Type X gypsum wallboard |
60 |
|
32 mm gypsum-sand plaster on metal lath |
60 |
D-2.3.13. Beams
D-2.3.14. Wired Glass Assembly Support
- not less than 6 mm thick;
- reinforced by a steel wire mesh in the form
of diamonds, squares or hexagons having dimensions of
- approximately 25 mm across the flats, using wire of not less than 0.45 mm diam, or
- approximately 13 mm across the flats, using wire of not less than 0.40 mm diam, the wire to be centrally embedded during manufacture and welded or intertwined at each intersection;
- set in fixed steel frames with metal not less than 1.35 mm thick and providing a glazing stop of not less than 20 mm on each side of the glass; and
- limited in area so that
- individual panes are not more than 0.84 m2, with neither height nor width more than 1.4 m, and
- the area not structurally supported by mullions is not more than 7.5 m2.
D-2.4. Solid Wood Walls, Floors and Roofs
D-2.4.1. Minimum Thickness
| Table D-2.4.1. Minimum Thickness of Solid Wood Walls, Roofs and Floors, mm(1)(2) Forming part of Article D-2.4.1. | ||||
| Type of Construction | Fire-Resistance Rating | |||
| 30 min | 45 min | 1 h | 1.5 h | |
|
Solid wood floor with building paper and finish flooring on top(3) |
89 | 114 | 165 | 235 |
| Solid wood, splined or tongued and grooved floor with building paper and finish flooring on top(4) | 64 | 76 | — | — |
|
Solid wood walls of loadbearing vertical plank(3) |
89 | 114 | 140 | 184 |
|
Solid wood walls of non-loadbearing horizontal plank(3) |
89 | 89 | 89 | 140 |
| Notes to Table D-2.4.1.: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | See CSA O141, “Softwood Lumber,” for sizes. |
| (2) | The fire-resistance ratings and minimum dimensions for floors also apply to solid wood roof decks of comparable thickness with finish roofing material. |
| (3) | The assembly shall consist of 38 mm thick members on edge fastened together with 101 mm common wire nails spaced not more than 400 mm o.c. and staggered in the direction of the grain. |
| (4) | The floor shall consist of 64 mm by 184 mm wide planks either tongued and grooved or with 19 mm by 38 mm splines set in grooves and fastened together with 88 mm common nails spaced not more than 400 mm o.c. |
D-2.4.2. Increased Fire-Resistance Rating
- 12.7 mm thick gypsum wallboard,
- 20 mm thick gypsum-sand plaster on metal lath, or
- 13 mm thick gypsum-sand plaster on 9.5 mm gypsum lath.
D-2.4.3. Supplementary Ratings
| Table D-2.4.3. Fire-Resistance Rating of Non-Loadbearing Built-up Solid Wood Partitions(1) Forming part of Article D-2.4.3. | ||
| Construction Details | Actual Overall Thickness, mm | Fire-Resistance Rating |
| Solid panels of wood boards 64 mm to 140 mm wide grooved and joined with wood splines, nailed together, boards placed vertically with staggered joints, 3 boards thick | 58 | 30 min |
| Solid panels with 4 mm plywood facings(2) glued to 46 mm solid wood core of glued, tongued and grooved construction for both sides and ends of core pieces with tongued and grooved rails in the core about 760 mm apart | 54 | 1 h |
D-2.5. Solid Plaster Partitions
D-2.5.1. Minimum Thickness
| Table D-2.5.1. Minimum Thickness of Non-Loadbearing Solid Plaster Partitions, mm Forming part of Article D-2.5.1. | |||||||
|
Type of Plaster on Metal Lath(1) | Fire-Resistance Rating | ||||||
| 30 min | 45 min | 1 h | 1.5 h | 2 h | 3 h | 4 h | |
| Portland cement-sand(2) or Portland cement-lime-sand |
50(3) |
— | — | — | — | — | — |
| Gypsum-sand |
50(3) |
50(3) |
64 | — | — | — | — |
| Gypsum-vermiculite, gypsum-perlite, Portland cement-vermiculite or Portland cement-perlite |
50(3) |
50(3) |
50(3) |
58 | 64 | 83 | 102 |
| Notes to Table D-2.5.1.: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | Metal lath shall be expanded metal lath or welded woven wire fabric supported on 19 mm vertical light steel studs spaced not more than 600 mm o.c. Plaster shall be applied to both sides of the lath. |
| (2) | For mixture of Portland cement-sand plaster, see D-1.7.2.(2). |
| (3) | CSA A82.30-M, “Interior Furring, Lathing and Gypsum Plastering,” does not permit solid plaster partitions less than 50 mm thick. |
D-2.6. Protected Steel Columns
D-2.6.1. Minimum Thickness of Protective Covering
| Table D-2.6.1.A. Minimum Thickness of Concrete or Masonry Protection to Steel Columns, mm Forming part of Article D-2.6.1. | |||||||
| Description of Cover | Fire-Resistance Rating | ||||||
| 30 min | 45 min | 1 h | 1.5 h | 2 h | 3 h | 4 h | |
| Monolithic concrete | |||||||
| Type S concrete(1) (column spaces filled)(2) | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 39 | 64 | 89 |
| Type N or L concrete(1) (column spaces filled)(2) | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 32 | 50 | 77 |
|
Concrete masonry units(3) or precast reinforced concrete units |
|||||||
| Type S concrete (column spaces not filled) | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 64 | 89 | 115 |
| Type N or L concrete (column spaces not filled) | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 77 | 102 |
| 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 64 | 77 | |
|
Clay or shale brick(4) (column spaces not filled) |
50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 77 | 102 |
|
50(6) |
50(6) |
50(6) |
50(6) |
||||
|
Hollow clay tile(5) (column spaces not filled) |
50(6) |
50(6) |
50(6) |
— | — | — | — |
| Notes to Table D-2.6.1.A.: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | Applies to cast-in-place concrete reinforced with 5.21 mm diam wire wrapped around column spirally 200 mm o.c., or 1.57 mm diam wire mesh with 100 mm by 100 mm openings. |
| (2) | The space between the protective covering and the web or flange of the column shall be filled with concrete, cement mortar or a mixture of cement mortar and broken bricks. |
| (3) | Concrete masonry shall be reinforced with 5.21 mm diam wire or wire mesh with 1.19 mm diam wire and 10 mm by 10 mm openings, laid in every second course. |
| (4) | Brick cover 77 mm thick or less shall be reinforced with 2.34 mm diam wire or 1.19 mm diam wire mesh with 10 mm by 10 mm openings, laid in every second course. |
| (5) | Hollow clay tiles and masonry mortar shall be reinforced with 1.19 mm diam wire mesh with 10 mm by 10 mm openings, laid in every horizontal joint and lapped at corners. |
| (6) | Hollow clay tiles shall conform to CSA A82.5-M, “Structural Clay Non-Load-Bearing Tile.” |
| (7) | 50 mm nominal hollow clay tile, reinforced with 1.19 mm diam wire mesh with 10 mm by 10 mm openings laid in every horizontal joint and covered with 19 mm gypsum-sand plaster and with limestone concrete fill in column spaces, has a 4 h fire-resistance rating. |
| Table D-2.6.1.B. Minimum Thickness of Plaster Protection to Steel Columns, mm Forming part of Article D-2.6.1. | |||||||
| Description | |||||||
| 30 min | 45 min | 1 h | 1.5 h | 2 h | 3 h | 4 h | |
| Gypsum-sand plaster on 9.5 mm gypsum lath(3) | 13 | 13 | 13 | 20 | — | — | — |
| Gypsum-perlite or vermiculite plaster on 9.5 mm gypsum lath(3) | 13 | 13 | 13 | 20 | 25 | — | — |
| Gypsum perlite or vermiculite plaster on 12.7 mm gypsum lath(3) | 13 | 13 | 13 | 20 | 25 | 32 | 50 |
| Gypsum perlite or vermiculite plaster on double 12.7 mm gypsum lath(3) | 13 | 13 | 13 | 20 | 25 | 25 | 32 |
| Portland cement-sand plaster on metal lath(4)(5) | 25 | 25 | 25 | — | — | — | — |
| Notes to Table D-2.6.1.B.: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | Fire-resistance ratings of 30 min and 45 min apply to columns whose M/D ratio is 30 or greater. Fire-resistance ratings greater than 45 min apply to columns whose M/D ratio is greater than 60. Where the M/D ratio is between 30 and 60 and the required fire-resistance rating is greater than 45 min, the total thickness of protection specified in the Table shall be increased by 50%. (To determine M/D, refer to Article D-2.6.4.) |
| (2) | Where the thickness of plaster over gypsum lath is 25 mm or more, wire mesh with 1.57 mm diam wire and openings not exceeding 50 mm by 50 mm shall be placed midway in the plaster. |
| (3) | Lath held in place by 1.19 mm diam wire wrapped around lath 450 mm o.c. |
| (4) | Expanded metal lath 1.36 kg/m 2 fastened to 9.5 mm by 19 mm steel channels held in vertical position around column by 1.19 mm diam wire ties. |
| (5) | For mixture of Portland cement-sand plaster, see D-1.7.2.(2). |
| Table D-2.6.1.C. Minimum Thickness of Gypsum-Sand Plaster on Metal Lath Protection to Steel Columns, mm Forming part of Article D-2.6.1. | ||||||
|
M/D(1) | Fire-Resistance Rating | |||||
| 30 min | 45 min | 1 h | 1.5 h | 2 h | 3 h | |
| 30 to 60 | 16 | 16 | 32 | — | — | — |
| over 60 to 90 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 32 | — | — |
| over 90 to 120 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 25 | 39 | — |
| over 120 to 180 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 25 | — |
| over 180 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 25 | 39 |
| Notes to Table D-2.6.1.C.: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | To determine the M/D ratio, refer to Article D-2.6.4. |
| Table D-2.6.1.D. Minimum Thickness of Gypsum-Perlite or Gypsum-Vermiculite Plaster on Metal Lath Protection to Steel Columns, mm Forming part of Article D-2.6.1. | |||||||
|
M/D(1) | Fire-Resistance Rating | ||||||
| 30 min | 45 min | 1 h | 1.5 h | 2 h | 3 h | 4 h | |
| 30 to 60 | 16 | 16 | 20 | 32 | 35 | — | — |
| over 60 to 90 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 20 | 26 | 35 | 45 |
| over 90 to 120 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 26 | 35 | 45 |
| over 120 to 180 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 20 | 32 | 35 |
| over 180 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 26 | 35 |
| Notes to Table D-2.6.1.D.: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | To determine the M/D ratio, refer to Article D-2.6.4. |
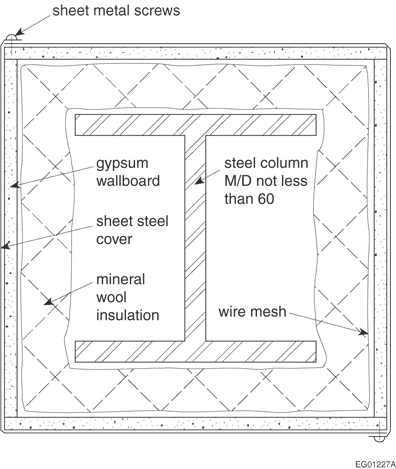
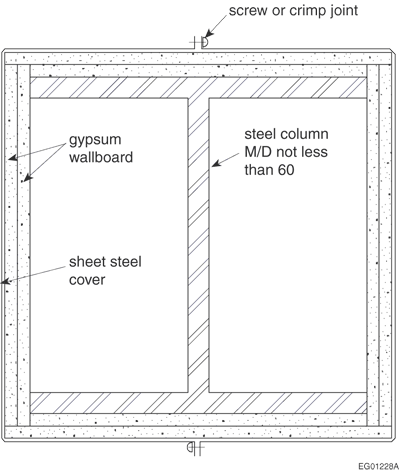
| Table D-2.6.1.E. Steel Columns with Sheet-Steel Membrane and Insulation as Shown in Figures D-2.6.1-A. and D-2.6.1-B. Forming part of Article D-2.6.1. | ||||
| Type of Protection |
Steel Thickness,(1) mm |
Fastening(2) | Insulation | Fire-Resistance Rating |
| See Figure D-2.6.1.-A | 0.51 |
No. 8 sheet-metal screws 9.5 mm long, 200 mm o.c. |
50 mm mineral wool batts(3) |
45 min |
| See Figure D-2.6.1.-B | 0.64 |
Self-threading screws or No. 8 sheet-metal screws, 600 mm o.c. |
2 layers 12.7 mm gypsum wallboard | 1.5 h |
| See Figure D-2.6.1.-A | 0.64 |
No. 8 sheet-metal screws, 9.5 mm long 200 mm o.c. |
75 mm mineral wool batts,(3) 12.7 mm gypsum wallboard |
2 h |
| See Figure D-2.6.1.-B | 0.76 |
Crimped joint or No. 8 sheet-metal screws, 300 mm o.c. |
2 layers 15.9 mm gypsum wallboard |
2 h |
| Notes to Table D-2.6.1.E.: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | Minimum thickness, galvanized or wiped-zinc-coated sheet-steel. |
| (2) | Sheet-steel shall be securely fastened to the floor and superstructure, or where sheet-steel cover does not extend floor to floor, fire stopping shall be provided at the level where sheet-steel protection ends. In the latter case, an alternate type of fire protection shall be applied between the fire stopping and the superstructure. |
| (3) | Conforming to CAN/ULC-S702, “Mineral Fibre Thermal Insulation for Buildings,” Type 1A, minimum density 30 kg/m3: column section and batts wrapped with 25 mm mesh chicken wire. |
| Table D-2.6.1.F. Minimum M/D Ratio for Steel Columns Covered with Type X Gypsum Wallboard Protection(1) Forming part of Article D-2.6.1. | ||||
|
Minimum Thickness of Type X Gypsum Wallboard Protection,(2) mm |
Fire-Resistance Rating | |||
| 1 h | 1.5 h | 2 h | 3 h | |
| 12.7 | 75 | — | — | — |
| 15.9 | 55 | — | — | — |
| 25.4 | 35 | 60 | — | — |
| 28.6 | 35 | 50 | — | — |
| 31.8 | 35 | 40 | 75 | — |
| 38.1 | 35 | 35 | 55 | — |
| 41.3 | 35 | 35 | 45 | — |
| 44.5 | 35 | 35 | 35 | — |
| 47.6 | 35 | 35 | 35 | — |
| 50.8 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 75 |
| 63.5 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 45 |
| Notes to Table D-2.6.1.F.: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | To determine the M/D ratio, refer to Article D-2.6.4. |
| (2) | See Article D-2.6.5. |
D-2.6.2. Hollow Unit Masonry Columns
D-2.6.3. Effect of Plaster
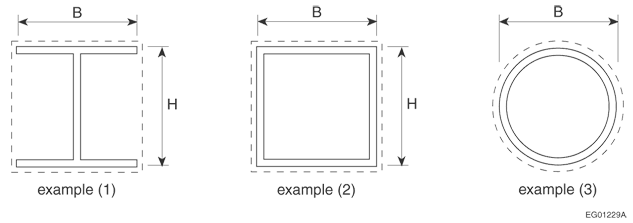
D-2.6.4. Determination of M/D Ratio
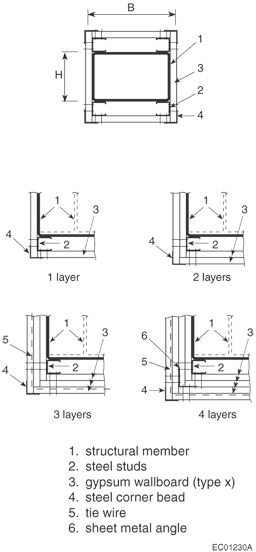
D-2.6.5. Attachment of Gypsum Wallboard
- be fabricated of galvanized steel that is not less than 0.41 mm thick,
- have legs not less than 31 mm long,
- be attached to the wallboard or stud with 25.4 mm screws spaced not more than 300 mm o.c., and
- have the attaching fasteners penetrate either another corner bead in multiple layer assemblies or the steel stud member.
D-2.6.6. Concrete Filled Hollow Steel Columns

- 1.0 C'r for plain concrete filling (PC),
- 1.1 C'r for steel-fibre reinforced concrete filling (FC), and
- 1.7 C'r for bar-reinforced concrete filling (RC),
- not less than 13 mm in diameter,
- located on opposite faces, 150 mm above or below a base plate, cap plate or concrete slab,
- orientated so that adjacent pairs are perpendicular, and
- not obstructed by other building elements.
| Table D-2.6.6.A. Values of Constant “a” Forming part of Article D-2.6.6. | ||||
| Filling Type |
Concrete Type(1) | Steel Reinforcement | Circular Columns | Square Columns |
| PC | S | n/a | 0.070 | 0.060 |
| FC | S | ≈ 2% | 0.075 | 0.065 |
| RC | S | 1.5%-3% | 0.080 | 0.070 |
| RC | S | 3%-5% | 0.085 | 0.075 |
| PC | N | n/a | 0.080 | 0.070 |
| FC | N | ≈ 2% | 0.085 | 0.075 |
| RC | N | 1.5%-3% | 0.090 | 0.080 |
| RC | N | 3%-5% | 0.095 | 0.085 |
| Notes to Table D-2.6.6.A.: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | See Subsection D-1.4., Types of Concrete. |
| Table D-2.6.6.B. Validity Limits Forming part of Article D-2.6.6. | |||
| Parameter | Type of Concrete Filling | ||
| PC | FC | RC | |
|
fc' (MPa) |
20 to 40 | 20 to 55 | 20 to 55 |
| D (round) (mm) | 140 to 410 | 140 to 410 | 165 to 410 |
| D (square) (mm) | 140 to 305 | 102 to 305 | 175 to 305 |
| Reinforcement (%) | n/a | ≈ 2% of the concrete mix by mass |
1.5% to 5% of cross-sectional area(1) |
| Concrete Cover (mm) | n/a | n/a | ≥ 25 |
| R (min) | ≤ 120 | ≤ 180 | ≤ 180 |
| KL (mm) | 2 000 to 4 000 | 2 000 to 4 500 | 2 000 to 4 500 |
|
Class(2) |
1, 2 or 3 | 1, 2 or 3 | 1, 2 or 3 |
| Notes to Table D-2.6.6.B.: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | Limits on size, number and spacing of bars and ties in accordance with CAN/CSA-A23.3, “Design of Concrete Structures.” |
| (2) | Classification of sections in accordance with CSA S16, “Design of Steel Structures.” |
D-2.7. Individually Protected Steel Beams
D-2.7.1. Minimum Thickness of Protective Covering
| Table D-2.7.1. Minimum Thickness of Cover to Individual Protected Steel Beams, mm(1) Forming part of Article D-2.7.1. | |||||||
| Description of Cover | Fire-Resistance Rating | ||||||
| 30 min | 45 min | 1 h | 1.5 h | 2 h | 3 h | 4 h | |
|
Type S concrete(2) (beam spaces filled solid) |
25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 32 | 50 | 64 |
|
Type N or L concrete(2) (beam spaces filled solid) |
25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 39 | 50 |
|
Gypsum-sand plaster on 9.5 mm gypsum lath(3) |
13 | 13 | 13 | 20 | — | — | — |
| Gypsum-perlite or vermiculite plaster on 9.5 mm gypsum lath(3) | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 25 | — | — |
| Gypsum-perlite or gypsum-vermiculite on 12.7 mm gypsum lath(3) | 13 | 13 | 13 | 20 | 25 | 39 | 50 |
| Gypsum-perlite or vermiculite plaster on double 12.7 mm gypsum lath(3) | 13 | 13 | 13 | 20 | 25 | 25 | 39 |
|
Portland cement-sand on metal lath(4) |
23 | 23 | 23 | — | — | — | — |
| Gypsum-sand on metal lath(4) (plaster in contact with lower flange) | 16 | 20 | 25 | 39 | — | — | — |
| Gypsum-sand on metal lath with air gap between plaster and lower flange(4) | 16 | 16 | 16 | 25 | 25 | — | — |
|
Gypsum-perlite or gypsum-vermiculite on metal lath(4) |
16 | 16 | 16 | 23 | 23 | 35 |
48(5) |
D-2.7.2. Types of Concrete
D-2.7.3. Effect of Plaster
D-2.7.4. Exceptions
D-2.7.5. Beam Protected by a Membrane
D-2.8. Reinforced Concrete Columns
D-2.8.1. Minimum Dimensions
D-2.8.2. Method
- 75 f (R + 1) for all Types L and L40S concrete,
- 80 f (R + 1) for Type S concrete when the design condition of the concrete column is defined in the second and fourth columns of Table D-2.8.2.,
- 80 f (R + 0.75) for Type N concrete when the design condition of the concrete column is defined in the second and fourth columns of Table D-2.8.2., and
- 100 f (R + 1) for Types S and N concrete when the design condition of the concrete
column is defined in the third column of Table D-2.8.2.wheref= the value shown in Table D-2.8.2.,R= the required fire-resistance rating in hours,k= the effective length factor obtained from CAN/CSA-A23.3, “Design of Concrete Structures,”h= the unsupported length of the column in metres, andp= the area of vertical reinforcement in the column as a percentage of the column area.
| Table D-2.8.2. Values of Factor f(1) Forming part of Article D-2.8.2. | |||
|
Overdesign Factor(2) |
Values of Factor f to be Used in Applying Article D-2.8.2. |
||
| Where kh is not more than 3.7 m |
Where kh is more than 3.7 m but not more than 7.3 m |
||
|
t is not more than 300 mm, |
All other cases(4) | ||
| 1.00 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.0 |
| 1.25 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 0.9 |
| 1.50 | 0.83 | 1.0 | 0.83 |
| Notes to Table D-2.8.2.: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | For conditions that do not fall within the limits described in Table D-2.8.2., further information may be obtained from Reference (7) in Subsection D-6.1. |
| (2) | Overdesign factor is the ratio of the calculated load carrying capacity of the column to the column strength required to carry the specified loads determined in conformance with CAN/CSA-A23.3, “Design of Concrete Structures.” |
| (3) | Where the factor f results in a t greater than 300 mm, the appropriate factor f for “All other cases” shall be applicable. |
| (4) | Where p is equal to or less than 3% and the factor f results in a t less than 300 mm, the minimum thickness shall be 300 mm. |
D-2.8.3. Minimum Thickness of Concrete Cover
D-2.8.4. Minimum Requirements
D-2.8.5. Addition of Plaster
D-2.8.6. Built-in Columns
D-2.9. Reinforced Concrete Beams
D-2.9.1. Minimum Cover Thickness
| Table D-2.9.1. Minimum Cover to Principal Steel Reinforcement in Reinforced Concrete Beams, mm Forming part of Article D-2.9.1. | |||||||
| Type of Concrete | Fire-Resistance Rating | ||||||
| 30 min | 45 min | 1 h | 1.5 h | 2 h | 3 h | 4 h | |
| Type S, N or L | 20 | 20 | 20 | 25 | 25 | 39 | 50 |
D-2.9.2. Maximum Rating
D-2.9.3. Beam Integrated in Floor or Roof Slab
D-2.9.4. Minimum Thickness
D-2.9.5. Effect of Plaster
D-2.10. Prestressed Concrete Beams
D-2.10.1. Minimum Cross-Sectional Area and Thickness of Cover
| Table D-2.10.1. Minimum Thickness of Concrete Cover over Steel Tendons in Prestressed Concrete Beams, mm(1) Forming part of Article D-2.10.1. | ||||||||
| Type of Concrete |
Area of Beam, cm2 |
Fire-Resistance Rating | ||||||
| 30 min | 45 min | 1 h | 1.5 h | 2 h | 3 h | 4 h | ||
| Type S or N | 260 to 970 | 25 | 39 | 50 | 64 | — | — | — |
| Over 970 to 1 940 | 25 | 26 | 39 | 45 | 64 | — | — | |
| Over 1 940 | 25 | 26 | 39 | 39 | 50 | 77 | 102 | |
| Type L | Over 970 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 39 | 50 | 77 | 102 |
D-2.10.2. Minimum Cover Thickness
D-2.10.3. Applicability of Ratings
D-2.10.4. Effect of Plaster
D-2.10.5. Minimum Cover
D-2.11. Glued-Laminated Timber Beams and Columns
D-2.11.1. Applicability of Information
D-2.11.2. Method of Calculation
- 0.1 fB [4 − 2(B/D)] for beams that may be exposed to fire on 4 sides,
- 0.1 fB [4 − (B/D)] for beams that may be exposed to fire on 3 sides,
- 0.1 fB [3 − (B/D)] for columns that may be exposed to fire on 4 sides, and
- 0.1 fB [3 − (B/2D)] for columns that may be exposed to fire on 3 sides,
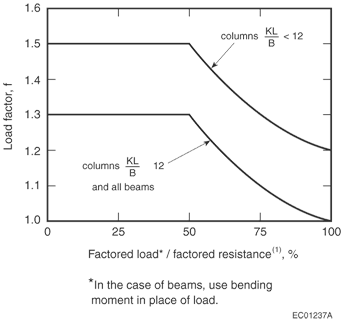
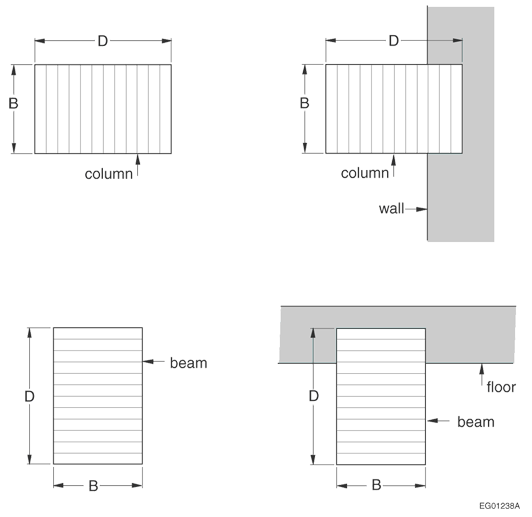
wheref= the load factor shown in Figure D-2.11.2.-A,B= the full dimension of the smaller side of a beam or column in millimetres before exposure to fire [see Figure D-2.11.2.-B],D= the full dimension of the larger side of a beam or column in millimetres before exposure to fire [see Figure D-2.11.2.-B],k= the effective length factor obtained from CSA O86, “Engineering Design in Wood,”L= the unsupported length of a column in millimetres.
|
|
|
| (1) |
See D-2.11.2.(2).
|
|
|
|
| (1) |
See D-2.11.2.(2).
|
|
|
|
| (1) | See D-2.11.2.(2). |
| (1) | See D-2.11.2.(2). |
Section D-3. Flame-Spread Ratings and Smoke Developed Classifications
D-3.1. Interior Finish Materials
D-3.1.1. Scope of Information
| Table D-3.1.1.A. Assigned Flame-Spread Ratings and Smoke Developed Classifications for Combinations of Wall and Ceiling Finish Materials and Surface Coatings(1) Forming part of Article D-3.1.1. | ||||
| Materials | Applicable Material Standard | Minimum Thickness, mm | Surface Coating | |
| Unfinished |
Paint or Varnish not more than 1.3 mm Thick, Cellulosic Wallpaper not more than One Layer(2)(3) | |||
| Brick, concrete, tile | None | None | 0/0 | 25/50 |
| Steel, copper, aluminum | None | 0.33 | ||
| Gypsum plaster | CSA A82.22-M | None | ||
| Gypsum wallboard | CAN/CSA-A82.27-M | 9.5 | 25/50 | 25/50 |
|
ASTM C 1396/C 1396M |
||||
| Lumber | None | 16 | 150/300 | 150/300 |
|
Douglas Fir plywood(4) |
CSA O121 | 11 | 150/100 | 150/300 |
|
Poplar plywood(4) |
CSA O153-M | |||
|
Plywood with Spruce face veneer(4) |
CSA O151 | |||
|
Douglas Fir plywood(4) |
CSA O121 | 6 | 150/100 | 150/100 |
| Fiberboard low density | CAN/ULC-S706 | 11 | X/100 | 150/100 |
| Hardboard | ||||
| Type 1 | CAN/CGSB-11.3-M | 9 | 150/X | |
| Standard | 6 | 150/300 | 150/300 | |
| Particleboard |
ANSI A208.1 |
12.7 | 150/300 | |
Waferboard,  OSB OSB |
CSA O437.0 |
— | (5) | (5) |
 CAN/CSA-O325 CAN/CSA-O325 | — |  (5) (5) |  (5) (5) | |
| Notes to Table D-3.1.1.A.: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | See D-1.1.1.(5) for standards used to assign flame-spread ratings and smoke developed classifications. |
| (2) | Flame-spread ratings and smoke developed classifications for paints and varnish are not applicable to shellac and lacquer. |
| (3) | Flame-spread ratings and smoke developed classifications for paints apply only to alkyd and latex paints. |
| (4) | The flame-spread ratings and smoke developed classifications shown are for those plywoods without a cellulose resin overlay. |
| (5) | Insufficient test information available. |
| Table D-3.1.1.B. Flame-Spread Ratings and Smoke-Developed Classifications for Combinations of Common Floor Finish Materials and Surface Coatings(1) Forming part of Article D-3.1.1. | ||
| Materials | Applicable Standard |
FSR/SDC(2) |
| Hardwood or softwood flooring either unfinished or finished with a spar or urethane varnish coating | None | 300/300 |
| Wool carpet (woven), pile weight not less than 1120 g/m2, applied with or without felt underlay(3) | CAN/CGSB-4.129 | 300/300 |
| Nylon carpet, pile weight not less than 610 g/m2 and not more than 800 g/m2, applied with or without felt underlay(3) | CAN/CGSB-4.129 | 300/500 |
| Nylon carpet, pile weight not less than 610 g/m2 and not more than 1355 g/m2, glued down to concrete | CAN/CGSB-4.129 | 300/500 |
| Wool/nylon blend carpet (woven) with not more than 20% nylon and pile weight not less than 1120 g/m2 | CAN/CGSB-4.129 | 300/500 |
| Nylon/wool blend carpet (woven) with not more than 50% wool, pile weight not less than 610 g/m2 and not more than 800 g/m2 | CAN/CGSB-4.129 | 300/500 |
| Polypropylene carpet, pile weight not less than 500 g/m2 and not more than 1200 g/m2, glued down to concrete | CAN/CGSB-4.129 | 300/500 |
| Notes to Table D-3.1.1.B.: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | Tested on the floor of the tunnel in conformance with provisions of CAN/ULC-S102.2, “Test for Surface Burning Characteristics of Flooring, Floor Coverings, and Miscellaneous Materials and Assemblies.” |
| (2) | Flame-Spread Rating/Smoke Developed Classification. |
| (3) | Type 1 or 2 underlay as described in CGSB 4-GP-36M, “Carpet Underlay, Fiber Type.” |
D-3.1.2. Ratings
D-3.1.3. Table Entries
D-3.1.4. Effect of Surface Coatings
D-3.1.5. Proprietary Materials
D-3.1.6. Limitations and Conditions
D-3.1.7. Referenced Standards
Section D-4. Noncombustibility
D-4.1. Test Method
D-4.1.1. Determination of Noncombustibility
D-4.2. Materials Classified as Combustible
D-4.2.1. Combustible Materials
D-4.2.2. Composite Materials
D-4.2.3. Effect of Chemical Additives
D-4.3. Materials Classified as Noncombustible
D-4.3.1. Typical Examples
Section D-5. Protection of Openings in Fire-Rated Assemblies
D-5.1. Scope
D-5.1.1. Installation Information
- the installation of fire doors and fire dampers in gypsum-wallboard-protected stud wall assemblies, and
- fire stop flaps for installation in fire-rated membrane ceilings.
D-5.2. Installation of Fire Doors and Fire Dampers
D-5.2.1. References
D-5.3. Fire Stop Flaps
D-5.3.1. Construction Requirements
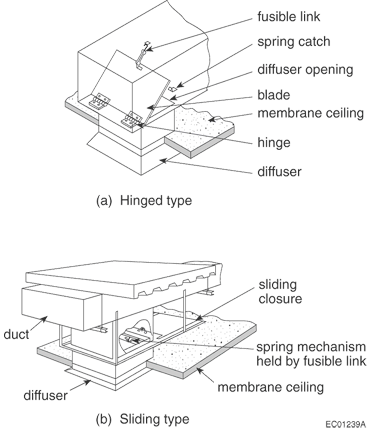
D-5.3.2. Hold-open Devices
Section D-6. Background Information
D-6.1. Fire Test Reports
D-6.2. Obsolete Materials and Assemblies
D-6.3. Assessment of Archaic Assemblies
D-6.4. Development of the Component Additive Method
- Since gypsum wallboard is used (D-2.3.4.(2) and Table D-2.3.4.A.) time assigned to 12.7 mm Type X gypsum wallboard membrane on the fire-exposed side of the partition = 25 min
- Time assigned to wood framing members at 400 mm o.c. (D-2.3.4.(3) and Table D-2.3.4.C.) = 20 min
- Time assigned to insulation, if the spaces between the studs are filled with preformed insulation of rock or slag fibres conforming to CAN/ULC-S702, “Mineral Fibre Thermal Insulation for Buildings,” (D-2.3.4.(4) and Table D-2.3.4.D.) = 15 min
- Time assigned to the membrane on the non-fire-exposed side (D-2.3.5.(1)) = 0 min
Fire-resistance rating = 25 + 20 + 15 = 60 min