Division B
Acceptable Solutions
Part 4 — Flammable and Combustible Liquids
Section 4.3. Tank Storage
4.3.1. Design, Construction and Use of Storage Tanks
4.3.1.1. Application
4.3.1.2. Atmospheric Storage Tanks
1)  Except as permitted in Sentence (3) and in Section 4.10., atmospheric storage tanks shall be built in conformance with the following:
Except as permitted in Sentence (3) and in Section 4.10., atmospheric storage tanks shall be built in conformance with the following:
 Except as permitted in Sentence (3) and in Section 4.10., atmospheric storage tanks shall be built in conformance with the following:
Except as permitted in Sentence (3) and in Section 4.10., atmospheric storage tanks shall be built in conformance with the following:k) CAN/ULC-S653, “Aboveground Steel Contained Tank Assemblies for Flammable and Combustible Liquids,”
2)  Tanks built in conformance with Clauses (1)(a), (b) and (c) shall be used only for the storage of crude petroleum at oil fields.
Tanks built in conformance with Clauses (1)(a), (b) and (c) shall be used only for the storage of crude petroleum at oil fields.
 Tanks built in conformance with Clauses (1)(a), (b) and (c) shall be used only for the storage of crude petroleum at oil fields.
Tanks built in conformance with Clauses (1)(a), (b) and (c) shall be used only for the storage of crude petroleum at oil fields. 3)  When necessitated by possible contamination of the liquid to be stored or possible rapid corrosion of the tank, storage tanks need not conform to Sentence (1), provided that they are designed and built in conformance with good engineering practice for the material being used.
When necessitated by possible contamination of the liquid to be stored or possible rapid corrosion of the tank, storage tanks need not conform to Sentence (1), provided that they are designed and built in conformance with good engineering practice for the material being used.
 When necessitated by possible contamination of the liquid to be stored or possible rapid corrosion of the tank, storage tanks need not conform to Sentence (1), provided that they are designed and built in conformance with good engineering practice for the material being used.
When necessitated by possible contamination of the liquid to be stored or possible rapid corrosion of the tank, storage tanks need not conform to Sentence (1), provided that they are designed and built in conformance with good engineering practice for the material being used.
4)  Atmospheric storage tanks shall not be used for the storage of flammable liquids or combustible liquids at temperatures at or above their boiling points.
Atmospheric storage tanks shall not be used for the storage of flammable liquids or combustible liquids at temperatures at or above their boiling points.
 Atmospheric storage tanks shall not be used for the storage of flammable liquids or combustible liquids at temperatures at or above their boiling points.
Atmospheric storage tanks shall not be used for the storage of flammable liquids or combustible liquids at temperatures at or above their boiling points.
4.3.1.3. Low Pressure Storage Tanks and Pressure Vessels
2) Pressure vessels shall be constructed in conformance with the British Columbia Power Engineers, Boiler, Pressure Vessel and
Refrigeration Safety Regulation.

3)  Low pressure storage tanks and pressure vessels are permitted to be used as atmospheric storage tanks.
Low pressure storage tanks and pressure vessels are permitted to be used as atmospheric storage tanks.
 Low pressure storage tanks and pressure vessels are permitted to be used as atmospheric storage tanks.
Low pressure storage tanks and pressure vessels are permitted to be used as atmospheric storage tanks. 4.3.1.4. Operating Pressure
1)  The normal operating pressure of a storage tank shall not exceed its design pressure.
The normal operating pressure of a storage tank shall not exceed its design pressure.
 The normal operating pressure of a storage tank shall not exceed its design pressure.
The normal operating pressure of a storage tank shall not exceed its design pressure.
4.3.1.5. Corrosion Protection
1)  The exposed surface of every aboveground storage tank for flammable liquids or combustible liquids that is fabricated of any ferrous substance shall be thoroughly coated with a rust-resisting
material that is compatible with the tank.
The exposed surface of every aboveground storage tank for flammable liquids or combustible liquids that is fabricated of any ferrous substance shall be thoroughly coated with a rust-resisting
material that is compatible with the tank.
 The exposed surface of every aboveground storage tank for flammable liquids or combustible liquids that is fabricated of any ferrous substance shall be thoroughly coated with a rust-resisting
material that is compatible with the tank.
The exposed surface of every aboveground storage tank for flammable liquids or combustible liquids that is fabricated of any ferrous substance shall be thoroughly coated with a rust-resisting
material that is compatible with the tank.
4.3.1.6. Floating Roofs
1)  Except for perimeter sealing material, floating roof assemblies or internal floating covers installed in storage tanks shall be constructed of metal or other materials and
designed in conformance with one of the tank construction standards
listed in this Subsection.
Except for perimeter sealing material, floating roof assemblies or internal floating covers installed in storage tanks shall be constructed of metal or other materials and
designed in conformance with one of the tank construction standards
listed in this Subsection.
 Except for perimeter sealing material, floating roof assemblies or internal floating covers installed in storage tanks shall be constructed of metal or other materials and
designed in conformance with one of the tank construction standards
listed in this Subsection.
Except for perimeter sealing material, floating roof assemblies or internal floating covers installed in storage tanks shall be constructed of metal or other materials and
designed in conformance with one of the tank construction standards
listed in this Subsection.
4.3.1.7. Identification
1)  A storage tank and its filling and emptying connections shall be identified in conformance with CPPI 1990, “Using the CPPI Colour-Symbol System to Mark Equipment and Vehicles for Product Identification.”
A storage tank and its filling and emptying connections shall be identified in conformance with CPPI 1990, “Using the CPPI Colour-Symbol System to Mark Equipment and Vehicles for Product Identification.”
 A storage tank and its filling and emptying connections shall be identified in conformance with CPPI 1990, “Using the CPPI Colour-Symbol System to Mark Equipment and Vehicles for Product Identification.”
A storage tank and its filling and emptying connections shall be identified in conformance with CPPI 1990, “Using the CPPI Colour-Symbol System to Mark Equipment and Vehicles for Product Identification.”4.3.1.8. Overfill Protection
1) 
 Except as required in Sentence (2),
Except as required in Sentence (2), a storage tank shall be prevented from being overfilled by providing
a storage tank shall be prevented from being overfilled by providing

 Except as required in Sentence (2),
Except as required in Sentence (2), a storage tank shall be prevented from being overfilled by providing
a storage tank shall be prevented from being overfilled by providinga) continuous supervision of the filling operations by personnel qualified to supervise such operations, or
b) an overfill protection device conforming to  ULC-S661, “Overfill Protection Devices for Flammable and Combustible Liquid Storage Tanks”
ULC-S661, “Overfill Protection Devices for Flammable and Combustible Liquid Storage Tanks” (see Appendix A).
(see Appendix A).
 ULC-S661, “Overfill Protection Devices for Flammable and Combustible Liquid Storage Tanks”
ULC-S661, “Overfill Protection Devices for Flammable and Combustible Liquid Storage Tanks” (see Appendix A).
(see Appendix A). 2) 
 Tight-filled storage tanks shall be prevented from being overfilled by providing a positive shut-off
device conforming to ULC-S661, “Overfill Protection Devices for Flammable and Combustible Liquid Storage Tanks” (See Appendix A.)
Tight-filled storage tanks shall be prevented from being overfilled by providing a positive shut-off
device conforming to ULC-S661, “Overfill Protection Devices for Flammable and Combustible Liquid Storage Tanks” (See Appendix A.)

 Tight-filled storage tanks shall be prevented from being overfilled by providing a positive shut-off
device conforming to ULC-S661, “Overfill Protection Devices for Flammable and Combustible Liquid Storage Tanks” (See Appendix A.)
Tight-filled storage tanks shall be prevented from being overfilled by providing a positive shut-off
device conforming to ULC-S661, “Overfill Protection Devices for Flammable and Combustible Liquid Storage Tanks” (See Appendix A.)
4.3.1.9. Installation and Use
1)  Unless otherwise specified in this Code, a storage tank shall be installed and used in conformance with the applicable installation and use provisions of the design document
to which the storage tank was built as required by this Section.
Unless otherwise specified in this Code, a storage tank shall be installed and used in conformance with the applicable installation and use provisions of the design document
to which the storage tank was built as required by this Section.
 Unless otherwise specified in this Code, a storage tank shall be installed and used in conformance with the applicable installation and use provisions of the design document
to which the storage tank was built as required by this Section.
Unless otherwise specified in this Code, a storage tank shall be installed and used in conformance with the applicable installation and use provisions of the design document
to which the storage tank was built as required by this Section.
4.3.1.10. Reuse
1)  A storage tank that has been taken out of service shall not be reused for the storage of flammable liquids or combustible liquids unless it has been
A storage tank that has been taken out of service shall not be reused for the storage of flammable liquids or combustible liquids unless it has been
 A storage tank that has been taken out of service shall not be reused for the storage of flammable liquids or combustible liquids unless it has been
A storage tank that has been taken out of service shall not be reused for the storage of flammable liquids or combustible liquids unless it has beena) refurbished so as to conform to one of the standards listed in Sentence 4.3.1.2.(1), or
b) refurbished in conformance with Sentence (2) or (3).
2)  A storage tank is permitted to be refurbished for aboveground use in conformance with one of the
following standards:
A storage tank is permitted to be refurbished for aboveground use in conformance with one of the
following standards:
 A storage tank is permitted to be refurbished for aboveground use in conformance with one of the
following standards:
A storage tank is permitted to be refurbished for aboveground use in conformance with one of the
following standards:
3)  A storage tank is permitted to be refurbished for underground use in conformance with one of the
following standards:
A storage tank is permitted to be refurbished for underground use in conformance with one of the
following standards: (See Appendix A.)
(See Appendix A.)
 A storage tank is permitted to be refurbished for underground use in conformance with one of the
following standards:
A storage tank is permitted to be refurbished for underground use in conformance with one of the
following standards: (See Appendix A.)
(See Appendix A.)
4)  A riveted storage tank shall not be relocated.
A riveted storage tank shall not be relocated.
 A riveted storage tank shall not be relocated.
A riveted storage tank shall not be relocated.
4.3.2. Installation of Outside Aboveground Storage Tanks
4.3.2.1. Location
1)  Every outside aboveground storage tank for the storage of flammable liquids or combustible liquids shall be located in conformance with Sentences (2) to (5) with respect to a property line or a building on the same property.
Every outside aboveground storage tank for the storage of flammable liquids or combustible liquids shall be located in conformance with Sentences (2) to (5) with respect to a property line or a building on the same property.
 Every outside aboveground storage tank for the storage of flammable liquids or combustible liquids shall be located in conformance with Sentences (2) to (5) with respect to a property line or a building on the same property.
Every outside aboveground storage tank for the storage of flammable liquids or combustible liquids shall be located in conformance with Sentences (2) to (5) with respect to a property line or a building on the same property. 2)  Except as provided in Sentences (6) and (7), every aboveground storage tank containing stable liquids and having a working pressure of not more than 17 kPa (gauge) shall be separated
from a property line or a building on the same property by distances
Except as provided in Sentences (6) and (7), every aboveground storage tank containing stable liquids and having a working pressure of not more than 17 kPa (gauge) shall be separated
from a property line or a building on the same property by distances
 Except as provided in Sentences (6) and (7), every aboveground storage tank containing stable liquids and having a working pressure of not more than 17 kPa (gauge) shall be separated
from a property line or a building on the same property by distances
Except as provided in Sentences (6) and (7), every aboveground storage tank containing stable liquids and having a working pressure of not more than 17 kPa (gauge) shall be separated
from a property line or a building on the same property by distancesa) half those in Table 4.3.2.1., where protection is provided against fire or explosion in the tank in conformance with Sentence 4.3.2.5.(2), or
b) equal to those in Table 4.3.2.1., where protection referred to in Clause (a) is not provided.
| Table 4.3.2.1. Location of Aboveground Storage Tanks Forming part of Sentences 4.3.2.1.(2), (3) and (4), and 4.9.2.1.(2) and (3) | |
| Maximum Tank Capacity, L |
Minimum Distance to a Property Line or to a Building on the Same Property, m |
| 250 000 | 3 |
| 500 000 | 4.5 |
| 2 500 000 | 9 |
| 5 000 000 | 12 |
| over 5 000 000 | 15 |
3)  Every aboveground storage tank containing unstable liquids and having a working pressure of not more than 17 kPa (gauge) shall be separated from a property line or a
building on the same property by distances
Every aboveground storage tank containing unstable liquids and having a working pressure of not more than 17 kPa (gauge) shall be separated from a property line or a
building on the same property by distances
 Every aboveground storage tank containing unstable liquids and having a working pressure of not more than 17 kPa (gauge) shall be separated from a property line or a
building on the same property by distances
Every aboveground storage tank containing unstable liquids and having a working pressure of not more than 17 kPa (gauge) shall be separated from a property line or a
building on the same property by distancesa) equal to those in Table 4.3.2.1., but not less than 7.5 m, where protection is provided against fire or explosion in the tank
in conformance with Sentence 4.3.2.5.(2), or
b) 3 times those in Table 4.3.2.1., but not less than 15 m, where protection referred to in Clause (a) is not provided.
4)  Every aboveground storage tank containing boil-over liquids shall be separated from a property line or a building on the same property by distances
Every aboveground storage tank containing boil-over liquids shall be separated from a property line or a building on the same property by distances
 Every aboveground storage tank containing boil-over liquids shall be separated from a property line or a building on the same property by distances
Every aboveground storage tank containing boil-over liquids shall be separated from a property line or a building on the same property by distancesa) 0.75 times those in Table 4.3.2.1., where protection is provided against fire or explosion in the tank in conformance with Sentence 4.3.2.5.(2), or
b) equal to those in Table 4.3.2.1., where protection referred to in Clause (a) is not provided.
(See Appendix A.)5)  Where a storage tank containing stable liquids or unstable liquids has a working pressure greater than 17 kPa (gauge), the distances
from a property line or a building on the same property shall be those specified in Sentences (2) and (3) multiplied by 1.5, but shall be not less than 7.5 m.
Where a storage tank containing stable liquids or unstable liquids has a working pressure greater than 17 kPa (gauge), the distances
from a property line or a building on the same property shall be those specified in Sentences (2) and (3) multiplied by 1.5, but shall be not less than 7.5 m.
 Where a storage tank containing stable liquids or unstable liquids has a working pressure greater than 17 kPa (gauge), the distances
from a property line or a building on the same property shall be those specified in Sentences (2) and (3) multiplied by 1.5, but shall be not less than 7.5 m.
Where a storage tank containing stable liquids or unstable liquids has a working pressure greater than 17 kPa (gauge), the distances
from a property line or a building on the same property shall be those specified in Sentences (2) and (3) multiplied by 1.5, but shall be not less than 7.5 m. 6)  The minimum distance required in Sentence (2) from a storage tank containing only Class II or IIIA liquids to a building on the same property is permitted to be reduced to
The minimum distance required in Sentence (2) from a storage tank containing only Class II or IIIA liquids to a building on the same property is permitted to be reduced to
 The minimum distance required in Sentence (2) from a storage tank containing only Class II or IIIA liquids to a building on the same property is permitted to be reduced to
The minimum distance required in Sentence (2) from a storage tank containing only Class II or IIIA liquids to a building on the same property is permitted to be reduced toa) 1.5 m provided the tank capacity is not more than 50 000 L, or
b) zero provided the tank capacity is not more than 2 500 L.
7)  The minimum distance required in Sentence (2) is permitted to be waived provided the storage tank is in conformance with ULC-S655, “Aboveground Protected Tank Assemblies for Flammable and Combustible Liquids.”
The minimum distance required in Sentence (2) is permitted to be waived provided the storage tank is in conformance with ULC-S655, “Aboveground Protected Tank Assemblies for Flammable and Combustible Liquids.”
 The minimum distance required in Sentence (2) is permitted to be waived provided the storage tank is in conformance with ULC-S655, “Aboveground Protected Tank Assemblies for Flammable and Combustible Liquids.”
The minimum distance required in Sentence (2) is permitted to be waived provided the storage tank is in conformance with ULC-S655, “Aboveground Protected Tank Assemblies for Flammable and Combustible Liquids.”8)  Where end failure of horizontal storage tanks may endanger adjacent property, the tanks shall be placed
with the longitudinal axis parallel to such property.
Where end failure of horizontal storage tanks may endanger adjacent property, the tanks shall be placed
with the longitudinal axis parallel to such property.
 Where end failure of horizontal storage tanks may endanger adjacent property, the tanks shall be placed
with the longitudinal axis parallel to such property.
Where end failure of horizontal storage tanks may endanger adjacent property, the tanks shall be placed
with the longitudinal axis parallel to such property.
4.3.2.2. Spacing between Storage Tanks
1)  Except as required in Sentences (2) and (3) and in Article 4.3.2.3., the minimum distance between every combination of 2 aboveground storage tanks shall be 0.25 times the sum of their diameters, but shall
be not less than 1 m.
Except as required in Sentences (2) and (3) and in Article 4.3.2.3., the minimum distance between every combination of 2 aboveground storage tanks shall be 0.25 times the sum of their diameters, but shall
be not less than 1 m.
 Except as required in Sentences (2) and (3) and in Article 4.3.2.3., the minimum distance between every combination of 2 aboveground storage tanks shall be 0.25 times the sum of their diameters, but shall
be not less than 1 m.
Except as required in Sentences (2) and (3) and in Article 4.3.2.3., the minimum distance between every combination of 2 aboveground storage tanks shall be 0.25 times the sum of their diameters, but shall
be not less than 1 m.
2)  The minimum distance between any 2 storage tanks, neither of which has a capacity of more than 250 000
L, shall be 1 m.
The minimum distance between any 2 storage tanks, neither of which has a capacity of more than 250 000
L, shall be 1 m.
 The minimum distance between any 2 storage tanks, neither of which has a capacity of more than 250 000
L, shall be 1 m.
The minimum distance between any 2 storage tanks, neither of which has a capacity of more than 250 000
L, shall be 1 m.
3)  Where either of 2 aboveground storage tanks contains unstable liquids, the distance required in Sentences (1) and (2) shall be doubled.
Where either of 2 aboveground storage tanks contains unstable liquids, the distance required in Sentences (1) and (2) shall be doubled.
 Where either of 2 aboveground storage tanks contains unstable liquids, the distance required in Sentences (1) and (2) shall be doubled.
Where either of 2 aboveground storage tanks contains unstable liquids, the distance required in Sentences (1) and (2) shall be doubled. 4.3.2.3. Clearances from Liquefied Petroleum Gas Cylinders and Tanks
1)  The minimum separation between a flammable liquid or combustible liquid storage tank and a liquefied petroleum gas cylinder or tank shall be 6 m.
The minimum separation between a flammable liquid or combustible liquid storage tank and a liquefied petroleum gas cylinder or tank shall be 6 m.
 The minimum separation between a flammable liquid or combustible liquid storage tank and a liquefied petroleum gas cylinder or tank shall be 6 m.
The minimum separation between a flammable liquid or combustible liquid storage tank and a liquefied petroleum gas cylinder or tank shall be 6 m.
2)  Secondary containments for flammable liquid and combustible liquid storage tanks shall not contain any liquefied petroleum gas cylinder or tank, and the centre line of the secondary containment wall shall
be
not less than
Secondary containments for flammable liquid and combustible liquid storage tanks shall not contain any liquefied petroleum gas cylinder or tank, and the centre line of the secondary containment wall shall
be
not less than
 Secondary containments for flammable liquid and combustible liquid storage tanks shall not contain any liquefied petroleum gas cylinder or tank, and the centre line of the secondary containment wall shall
be
not less than
Secondary containments for flammable liquid and combustible liquid storage tanks shall not contain any liquefied petroleum gas cylinder or tank, and the centre line of the secondary containment wall shall
be
not less thana) 3 m away from a liquefied petroleum gas cylinder, and
b) 6 m away from a liquefied petroleum gas tank.
4.3.2.4. Fire Department Access
1)  Except as provided in Sentences (2) and (3), storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids shall be spaced so that each storage tank is accessible for firefighting purposes.
Except as provided in Sentences (2) and (3), storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids shall be spaced so that each storage tank is accessible for firefighting purposes.
 Except as provided in Sentences (2) and (3), storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids shall be spaced so that each storage tank is accessible for firefighting purposes.
Except as provided in Sentences (2) and (3), storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids shall be spaced so that each storage tank is accessible for firefighting purposes.
2) An access route constructed in conformance with Subsection
3.2.5. of Division B of the British Columbia Building Code shall be provided in outdoor
storage
areas to permit the approach of fire department vehicles to within 60 m
travelling distance of any storage tank.

3)  Where firefighting access to storage tanks containing Class I or II liquids is not provided, fire extinguishing measures conforming to Sentence 4.3.2.5.(2) shall be provided.
Where firefighting access to storage tanks containing Class I or II liquids is not provided, fire extinguishing measures conforming to Sentence 4.3.2.5.(2) shall be provided.
 Where firefighting access to storage tanks containing Class I or II liquids is not provided, fire extinguishing measures conforming to Sentence 4.3.2.5.(2) shall be provided.
Where firefighting access to storage tanks containing Class I or II liquids is not provided, fire extinguishing measures conforming to Sentence 4.3.2.5.(2) shall be provided. 4.3.2.5. Fire Protection Systems
(See Appendix A.)1)  Where the diameter of a storage tank exceeds 45 m, the storage tank shall be provided with protection against fires or explosions in conformance with Sentence (2).
Where the diameter of a storage tank exceeds 45 m, the storage tank shall be provided with protection against fires or explosions in conformance with Sentence (2).
 Where the diameter of a storage tank exceeds 45 m, the storage tank shall be provided with protection against fires or explosions in conformance with Sentence (2).
Where the diameter of a storage tank exceeds 45 m, the storage tank shall be provided with protection against fires or explosions in conformance with Sentence (2). 2)  Protection against fires or explosions required for a storage tank shall consist of fixed protection systems designed in conformance with good engineering practice such
as that described in
Protection against fires or explosions required for a storage tank shall consist of fixed protection systems designed in conformance with good engineering practice such
as that described in
 Protection against fires or explosions required for a storage tank shall consist of fixed protection systems designed in conformance with good engineering practice such
as that described in
Protection against fires or explosions required for a storage tank shall consist of fixed protection systems designed in conformance with good engineering practice such
as that described in 4.3.3. Supports, Foundations and Anchorage for Aboveground Storage Tanks
4.3.3.1. Foundations and Supports
1)  Storage tanks shall rest on the ground or on foundations, supports or piling made of concrete, masonry
or steel.
Storage tanks shall rest on the ground or on foundations, supports or piling made of concrete, masonry
or steel.
 Storage tanks shall rest on the ground or on foundations, supports or piling made of concrete, masonry
or steel.
Storage tanks shall rest on the ground or on foundations, supports or piling made of concrete, masonry
or steel.
2)  Tank supports shall be installed on firm foundations designed to minimize uneven settling of the tank and to minimize corrosion
of the part of the tank resting on the foundation.
Tank supports shall be installed on firm foundations designed to minimize uneven settling of the tank and to minimize corrosion
of the part of the tank resting on the foundation.
 Tank supports shall be installed on firm foundations designed to minimize uneven settling of the tank and to minimize corrosion
of the part of the tank resting on the foundation.
Tank supports shall be installed on firm foundations designed to minimize uneven settling of the tank and to minimize corrosion
of the part of the tank resting on the foundation.
3) 
 Where the clearance below the base of the tank exceeds
Where the clearance below the base of the tank exceeds 300 mm,
300 mm,  tank supports
tank supports shall have a minimum fire-resistance rating of 2 h.
shall have a minimum fire-resistance rating of 2 h.

 Where the clearance below the base of the tank exceeds
Where the clearance below the base of the tank exceeds 300 mm,
300 mm,  tank supports
tank supports shall have a minimum fire-resistance rating of 2 h.
shall have a minimum fire-resistance rating of 2 h. 4)  Every aboveground storage tank shall be supported in a manner that will prevent the allowable design stress
of the tank from being exceeded.
Every aboveground storage tank shall be supported in a manner that will prevent the allowable design stress
of the tank from being exceeded.
 Every aboveground storage tank shall be supported in a manner that will prevent the allowable design stress
of the tank from being exceeded.
Every aboveground storage tank shall be supported in a manner that will prevent the allowable design stress
of the tank from being exceeded.
4.3.3.2. Earthquake Protection
1) In areas subject to earthquake forces, storage tanks, supports and connections shall be designed to resist such forces in conformance
with
a) Part 4 of Division B of the British Columbia Building Code, and
b) Appendix  A2 of CAN/ULC-S601, “Shop Fabricated Steel Aboveground Tanks for Flammable and Combustible Liquids.”
A2 of CAN/ULC-S601, “Shop Fabricated Steel Aboveground Tanks for Flammable and Combustible Liquids.”
 A2 of CAN/ULC-S601, “Shop Fabricated Steel Aboveground Tanks for Flammable and Combustible Liquids.”
A2 of CAN/ULC-S601, “Shop Fabricated Steel Aboveground Tanks for Flammable and Combustible Liquids.”

4.3.3.3. Protection against Flooding
1)  When aboveground storage tanks are located in an area that is subject to flooding, the tanks shall be
securely anchored to prevent floating.
When aboveground storage tanks are located in an area that is subject to flooding, the tanks shall be
securely anchored to prevent floating.
 When aboveground storage tanks are located in an area that is subject to flooding, the tanks shall be
securely anchored to prevent floating.
When aboveground storage tanks are located in an area that is subject to flooding, the tanks shall be
securely anchored to prevent floating.
4.3.4. Normal and Emergency Venting for Aboveground Storage Tanks
4.3.4.1. Design and Installation
1)  Atmospheric and low pressure storage tanks shall be provided with normal and emergency venting in conformance with
Atmospheric and low pressure storage tanks shall be provided with normal and emergency venting in conformance with
 Atmospheric and low pressure storage tanks shall be provided with normal and emergency venting in conformance with
Atmospheric and low pressure storage tanks shall be provided with normal and emergency venting in conformance witha) API 2000, “Venting Atmospheric and Low-Pressure Storage Tanks: Nonrefrigerated and Refrigerated,” or
b) the tank design standards listed in Sentence 4.3.1.2.(1).
4.3.4.2. Unstable Liquids
1)  When unstable liquids are stored, the effects of heat or gas resulting from polymerization, decomposition,
condensation or self-reactivity shall be allowed for in the determination
of the total venting capacity.
When unstable liquids are stored, the effects of heat or gas resulting from polymerization, decomposition,
condensation or self-reactivity shall be allowed for in the determination
of the total venting capacity.
 When unstable liquids are stored, the effects of heat or gas resulting from polymerization, decomposition,
condensation or self-reactivity shall be allowed for in the determination
of the total venting capacity.
When unstable liquids are stored, the effects of heat or gas resulting from polymerization, decomposition,
condensation or self-reactivity shall be allowed for in the determination
of the total venting capacity.
4.3.5. Vent Piping for Aboveground Storage Tanks
4.3.5.1. Materials and Construction
1)  Except at distilleries covered in Section 4.10., vent piping materials and construction shall conform to Subsections 4.5.2., 4.5.3. and 4.5.5.
Except at distilleries covered in Section 4.10., vent piping materials and construction shall conform to Subsections 4.5.2., 4.5.3. and 4.5.5.
 Except at distilleries covered in Section 4.10., vent piping materials and construction shall conform to Subsections 4.5.2., 4.5.3. and 4.5.5.
Except at distilleries covered in Section 4.10., vent piping materials and construction shall conform to Subsections 4.5.2., 4.5.3. and 4.5.5.4.3.5.2. Location of Vent Pipe Outlets
1)  Normal vent pipe outlets for storage tanks of Class I liquids
Normal vent pipe outlets for storage tanks of Class I liquids
 Normal vent pipe outlets for storage tanks of Class I liquids
Normal vent pipe outlets for storage tanks of Class I liquidsa) shall be located outside buildings not less than
i) 3.5 m above the adjacent ground level, and
ii) 1.5 m from any building opening, and
2)  Normal vent pipe outlets for storage tanks of Class II or IIIA liquids shall discharge outside buildings not less than
Normal vent pipe outlets for storage tanks of Class II or IIIA liquids shall discharge outside buildings not less than
 Normal vent pipe outlets for storage tanks of Class II or IIIA liquids shall discharge outside buildings not less than
Normal vent pipe outlets for storage tanks of Class II or IIIA liquids shall discharge outside buildings not less thana) 2 m above the adjacent ground level, and
b) 1.5 m from any building opening.
3)  Emergency vent outlets for storage tanks shall discharge outside buildings not less than 1.5 m from any building opening and from any combustible component of any building's exterior wall.
Emergency vent outlets for storage tanks shall discharge outside buildings not less than 1.5 m from any building opening and from any combustible component of any building's exterior wall.
 Emergency vent outlets for storage tanks shall discharge outside buildings not less than 1.5 m from any building opening and from any combustible component of any building's exterior wall.
Emergency vent outlets for storage tanks shall discharge outside buildings not less than 1.5 m from any building opening and from any combustible component of any building's exterior wall.
4.3.5.3. Interconnection of Vent Piping
1)  Except as provided in Sentence (2), 2 or more storage tanks are permitted to be connected to a common vent pipe for normal relief venting provided
the vent pipe size is designed to vent the combined vapours produced
in the connected tanks without exceeding the allowable stresses of
the tanks.
Except as provided in Sentence (2), 2 or more storage tanks are permitted to be connected to a common vent pipe for normal relief venting provided
the vent pipe size is designed to vent the combined vapours produced
in the connected tanks without exceeding the allowable stresses of
the tanks.
 Except as provided in Sentence (2), 2 or more storage tanks are permitted to be connected to a common vent pipe for normal relief venting provided
the vent pipe size is designed to vent the combined vapours produced
in the connected tanks without exceeding the allowable stresses of
the tanks.
Except as provided in Sentence (2), 2 or more storage tanks are permitted to be connected to a common vent pipe for normal relief venting provided
the vent pipe size is designed to vent the combined vapours produced
in the connected tanks without exceeding the allowable stresses of
the tanks.
2)  Vent piping for storage tanks for Class I liquids shall not be connected to vent piping for storage tanks for Class II or IIIA liquids unless an effective arrangement is provided to prevent the vapours
from the Class I liquids from entering the other tanks.
Vent piping for storage tanks for Class I liquids shall not be connected to vent piping for storage tanks for Class II or IIIA liquids unless an effective arrangement is provided to prevent the vapours
from the Class I liquids from entering the other tanks.
 Vent piping for storage tanks for Class I liquids shall not be connected to vent piping for storage tanks for Class II or IIIA liquids unless an effective arrangement is provided to prevent the vapours
from the Class I liquids from entering the other tanks.
Vent piping for storage tanks for Class I liquids shall not be connected to vent piping for storage tanks for Class II or IIIA liquids unless an effective arrangement is provided to prevent the vapours
from the Class I liquids from entering the other tanks.
4.3.6. Openings Other than Vents in Aboveground Storage Tanks
4.3.6.1. Provision of Valves
1)  Each connection to an aboveground storage tank through which the liquid can normally flow shall be provided
with an internal or external shut-off valve located as close as practical
to the shell of the tank.
Each connection to an aboveground storage tank through which the liquid can normally flow shall be provided
with an internal or external shut-off valve located as close as practical
to the shell of the tank.
 Each connection to an aboveground storage tank through which the liquid can normally flow shall be provided
with an internal or external shut-off valve located as close as practical
to the shell of the tank.
Each connection to an aboveground storage tank through which the liquid can normally flow shall be provided
with an internal or external shut-off valve located as close as practical
to the shell of the tank.
2)  Each connection to an aboveground storage tank that is below the liquid level and through which liquid
does not normally flow shall be provided with a liquid-tight closing
device.
Each connection to an aboveground storage tank that is below the liquid level and through which liquid
does not normally flow shall be provided with a liquid-tight closing
device.
 Each connection to an aboveground storage tank that is below the liquid level and through which liquid
does not normally flow shall be provided with a liquid-tight closing
device.
Each connection to an aboveground storage tank that is below the liquid level and through which liquid
does not normally flow shall be provided with a liquid-tight closing
device.
4.3.6.2. Materials
1)  Valves and their connections to a storage tank shall be made of steel, except that when the chemical
characteristics of the liquid stored are incompatible with steel,
materials other than steel are permitted to be used.
Valves and their connections to a storage tank shall be made of steel, except that when the chemical
characteristics of the liquid stored are incompatible with steel,
materials other than steel are permitted to be used.
 Valves and their connections to a storage tank shall be made of steel, except that when the chemical
characteristics of the liquid stored are incompatible with steel,
materials other than steel are permitted to be used.
Valves and their connections to a storage tank shall be made of steel, except that when the chemical
characteristics of the liquid stored are incompatible with steel,
materials other than steel are permitted to be used.
2)  Materials for valves and their connections to a storage tank shall be suitable for the pressures, stresses and temperatures that may be expected, including those of
possible fire exposure.
Materials for valves and their connections to a storage tank shall be suitable for the pressures, stresses and temperatures that may be expected, including those of
possible fire exposure.
 Materials for valves and their connections to a storage tank shall be suitable for the pressures, stresses and temperatures that may be expected, including those of
possible fire exposure.
Materials for valves and their connections to a storage tank shall be suitable for the pressures, stresses and temperatures that may be expected, including those of
possible fire exposure.
4.3.6.3. Openings for Liquid Level Measurements
1)  Openings for measuring liquid levels in storage tanks for Class I liquids shall be equipped with caps or covers which shall be opened only when measuring the liquid level.
Openings for measuring liquid levels in storage tanks for Class I liquids shall be equipped with caps or covers which shall be opened only when measuring the liquid level.
 Openings for measuring liquid levels in storage tanks for Class I liquids shall be equipped with caps or covers which shall be opened only when measuring the liquid level.
Openings for measuring liquid levels in storage tanks for Class I liquids shall be equipped with caps or covers which shall be opened only when measuring the liquid level.
4.3.6.4. Connections for Filling and Emptying
1)  Except as provided in Sentence (3), connections used as part of normal operating conditions for filling or emptying storage tanks for flammable liquids and combustible liquids shall be located
Except as provided in Sentence (3), connections used as part of normal operating conditions for filling or emptying storage tanks for flammable liquids and combustible liquids shall be located
 Except as provided in Sentence (3), connections used as part of normal operating conditions for filling or emptying storage tanks for flammable liquids and combustible liquids shall be located
Except as provided in Sentence (3), connections used as part of normal operating conditions for filling or emptying storage tanks for flammable liquids and combustible liquids shall be locateda) outside buildings,
b) at a location free of sources of ignition, and
c) not less than 1.5 m away from building openings.
2)  Connections for filling or emptying storage tanks shall be kept closed to prevent leakage when not in use.
Connections for filling or emptying storage tanks shall be kept closed to prevent leakage when not in use.
 Connections for filling or emptying storage tanks shall be kept closed to prevent leakage when not in use.
Connections for filling or emptying storage tanks shall be kept closed to prevent leakage when not in use.
3)  A filling connection described in Sentence (1) is permitted to be located inside a building if
A filling connection described in Sentence (1) is permitted to be located inside a building if
 A filling connection described in Sentence (1) is permitted to be located inside a building if
A filling connection described in Sentence (1) is permitted to be located inside a building ifa) this is made necessary
i) by a process or activity located indoors and to which the tank is directly associated, or
ii) for the collection of used liquids, and
b) the fill piping is provided with means to prevent flammable
vapours from returning to the building.
4.3.7. Secondary Containment for Aboveground Storage Tanks
4.3.7.1. General
1)  The area surrounding a storage tank or group of storage tanks shall be designed to accommodate accidental spillage in conformance with Subsection 4.1.6.
The area surrounding a storage tank or group of storage tanks shall be designed to accommodate accidental spillage in conformance with Subsection 4.1.6.
 The area surrounding a storage tank or group of storage tanks shall be designed to accommodate accidental spillage in conformance with Subsection 4.1.6.
The area surrounding a storage tank or group of storage tanks shall be designed to accommodate accidental spillage in conformance with Subsection 4.1.6.2)  Where barriers described in Sentence 4.1.6.1.(1) are provided to contain accidental spillage from aboveground storage tanks, they shall conform to the requirements for secondary containment in this Subsection.
Where barriers described in Sentence 4.1.6.1.(1) are provided to contain accidental spillage from aboveground storage tanks, they shall conform to the requirements for secondary containment in this Subsection.
 Where barriers described in Sentence 4.1.6.1.(1) are provided to contain accidental spillage from aboveground storage tanks, they shall conform to the requirements for secondary containment in this Subsection.
Where barriers described in Sentence 4.1.6.1.(1) are provided to contain accidental spillage from aboveground storage tanks, they shall conform to the requirements for secondary containment in this Subsection.
3)  A storage tank conforming to Sentence 4.3.7.4.(2) shall be considered as conforming to this Subsection provided it is used and maintained in conformance with Articles 4.3.7.8. and 4.3.7.9.
A storage tank conforming to Sentence 4.3.7.4.(2) shall be considered as conforming to this Subsection provided it is used and maintained in conformance with Articles 4.3.7.8. and 4.3.7.9.
 A storage tank conforming to Sentence 4.3.7.4.(2) shall be considered as conforming to this Subsection provided it is used and maintained in conformance with Articles 4.3.7.8. and 4.3.7.9.
A storage tank conforming to Sentence 4.3.7.4.(2) shall be considered as conforming to this Subsection provided it is used and maintained in conformance with Articles 4.3.7.8. and 4.3.7.9.4.3.7.2. Construction
1)  Except as provided in Sentence (2), the base and walls of a secondary containment shall be made of noncombustible materials, and shall be designed, constructed and maintained
to
Except as provided in Sentence (2), the base and walls of a secondary containment shall be made of noncombustible materials, and shall be designed, constructed and maintained
to
 Except as provided in Sentence (2), the base and walls of a secondary containment shall be made of noncombustible materials, and shall be designed, constructed and maintained
to
Except as provided in Sentence (2), the base and walls of a secondary containment shall be made of noncombustible materials, and shall be designed, constructed and maintained
toa) withstand full hydrostatic head, and
b) provide a permeability of not more than 10-6 cm/s to the flammable liquids or combustible liquids contained in the storage tanks.
2)  Where a membrane providing the level of impermeability required in
Where a membrane providing the level of impermeability required in  Clause (1)(b) is combustible, it shall be covered with a noncombustible material of such nature
and thickness that the membrane will not fail when the secondary containment
is exposed to fire.
Clause (1)(b) is combustible, it shall be covered with a noncombustible material of such nature
and thickness that the membrane will not fail when the secondary containment
is exposed to fire.
 Where a membrane providing the level of impermeability required in
Where a membrane providing the level of impermeability required in  Clause (1)(b) is combustible, it shall be covered with a noncombustible material of such nature
and thickness that the membrane will not fail when the secondary containment
is exposed to fire.
Clause (1)(b) is combustible, it shall be covered with a noncombustible material of such nature
and thickness that the membrane will not fail when the secondary containment
is exposed to fire.
3)  Except as provided in Sentence (4), openings shall not be permitted in a secondary containment.
Except as provided in Sentence (4), openings shall not be permitted in a secondary containment.
 Except as provided in Sentence (4), openings shall not be permitted in a secondary containment.
Except as provided in Sentence (4), openings shall not be permitted in a secondary containment. 4)  Where piping passes through a secondary containment, such passages shall conform to Sentences (1) and (2).
Where piping passes through a secondary containment, such passages shall conform to Sentences (1) and (2).
 Where piping passes through a secondary containment, such passages shall conform to Sentences (1) and (2).
Where piping passes through a secondary containment, such passages shall conform to Sentences (1) and (2). 4.3.7.3. Capacity
(See A-4.1.6.1.(1) in Appendix A.)1)  Except as permitted in Sentence (3), a secondary containment for a single storage tank shall have a volumetric capacity of not less than 110%
of the capacity of the tank.
Except as permitted in Sentence (3), a secondary containment for a single storage tank shall have a volumetric capacity of not less than 110%
of the capacity of the tank.
 Except as permitted in Sentence (3), a secondary containment for a single storage tank shall have a volumetric capacity of not less than 110%
of the capacity of the tank.
Except as permitted in Sentence (3), a secondary containment for a single storage tank shall have a volumetric capacity of not less than 110%
of the capacity of the tank.
2)  Except as permitted in Sentence (3), a secondary containment for more than one storage tank shall have a volumetric capacity of not less than the sum of
Except as permitted in Sentence (3), a secondary containment for more than one storage tank shall have a volumetric capacity of not less than the sum of
 Except as permitted in Sentence (3), a secondary containment for more than one storage tank shall have a volumetric capacity of not less than the sum of
Except as permitted in Sentence (3), a secondary containment for more than one storage tank shall have a volumetric capacity of not less than the sum ofa) the capacity of the largest storage tank located in the contained space, and
b) 10% of the greater of
i) the capacity specified in Clause (a), or
ii) the aggregate capacity of all other storage tanks located in the contained space.
3)  When the secondary containment is designed to prevent the entry of precipitation and water used for firefighting purposes into the
contained space, it shall have a volumetric capacity of not less than
the capacity of the largest storage tank located in the contained space.
When the secondary containment is designed to prevent the entry of precipitation and water used for firefighting purposes into the
contained space, it shall have a volumetric capacity of not less than
the capacity of the largest storage tank located in the contained space.
 When the secondary containment is designed to prevent the entry of precipitation and water used for firefighting purposes into the
contained space, it shall have a volumetric capacity of not less than
the capacity of the largest storage tank located in the contained space.
When the secondary containment is designed to prevent the entry of precipitation and water used for firefighting purposes into the
contained space, it shall have a volumetric capacity of not less than
the capacity of the largest storage tank located in the contained space. 4.3.7.4. Clearances
1)  Except as provided in Sentence (2), no part of a secondary containment wall shall be less than 1.5 m from a storage tank shell.
Except as provided in Sentence (2), no part of a secondary containment wall shall be less than 1.5 m from a storage tank shell.
 Except as provided in Sentence (2), no part of a secondary containment wall shall be less than 1.5 m from a storage tank shell.
Except as provided in Sentence (2), no part of a secondary containment wall shall be less than 1.5 m from a storage tank shell. 2)  It is permitted to waive the distance required in Sentence (1) provided the storage tank
It is permitted to waive the distance required in Sentence (1) provided the storage tank
 It is permitted to waive the distance required in Sentence (1) provided the storage tank
It is permitted to waive the distance required in Sentence (1) provided the storage tanka) is constructed in accordance with
i) Clauses 4.3.1.2.(1)(j), (k), (l) or (m), incorporating secondary containment, or
ii) Clause 4.3.1.2.(1)(e) for double-walled storage tanks,
b) has a capacity of not more than 50 000 L, and
c) is protected by posts or guardrails when exposed to collision
damage.
4.3.7.5. Access to Storage Tanks and Ancillary Equipment
1)  A secondary containment shall permit
A secondary containment shall permit
 A secondary containment shall permit
A secondary containment shall permita) access to storage tanks, valves and ancillary equipment,
b) egress from the contained space, and
c) access for firefighting as specified in Article 4.3.2.4.
(See Appendix A.)2)  Where a storage tank contains Class I liquids, provisions shall be made for the normal operation of valves
and for access to the storage tank roof without entering the contained space created by the secondary containment
when
Where a storage tank contains Class I liquids, provisions shall be made for the normal operation of valves
and for access to the storage tank roof without entering the contained space created by the secondary containment
when
 Where a storage tank contains Class I liquids, provisions shall be made for the normal operation of valves
and for access to the storage tank roof without entering the contained space created by the secondary containment
when
Where a storage tank contains Class I liquids, provisions shall be made for the normal operation of valves
and for access to the storage tank roof without entering the contained space created by the secondary containment
whena) the average height of the secondary containment exceeds 3.5 m, measured from the ground level of the interior of
the contained area, or
b) the distance between the tank shell and the top inside edge
of the secondary containment wall is less than the height of this
wall.
(See Appendix A.)4.3.7.6. Emergency Venting
1)  Where the secondary containment is not open to the atmosphere, emergency venting shall be provided to relieve any buildup of internal
pressure in the contained space when exposed to heat or fire.
Where the secondary containment is not open to the atmosphere, emergency venting shall be provided to relieve any buildup of internal
pressure in the contained space when exposed to heat or fire.
 Where the secondary containment is not open to the atmosphere, emergency venting shall be provided to relieve any buildup of internal
pressure in the contained space when exposed to heat or fire.
Where the secondary containment is not open to the atmosphere, emergency venting shall be provided to relieve any buildup of internal
pressure in the contained space when exposed to heat or fire.
4.3.7.7. Leak Detection
1)  Where the contained space created by the secondary containment is not accessible for an internal visual examination,
Where the contained space created by the secondary containment is not accessible for an internal visual examination,  and the secondary containment is not sloped so as to permit liquid to flow to a specific location that can be monitored
and the secondary containment is not sloped so as to permit liquid to flow to a specific location that can be monitored , a monitoring device shall be provided to indicate the loss of integrity
of the secondary containment.
, a monitoring device shall be provided to indicate the loss of integrity
of the secondary containment.
 Where the contained space created by the secondary containment is not accessible for an internal visual examination,
Where the contained space created by the secondary containment is not accessible for an internal visual examination,  and the secondary containment is not sloped so as to permit liquid to flow to a specific location that can be monitored
and the secondary containment is not sloped so as to permit liquid to flow to a specific location that can be monitored , a monitoring device shall be provided to indicate the loss of integrity
of the secondary containment.
, a monitoring device shall be provided to indicate the loss of integrity
of the secondary containment.
4.3.7.8. Drainage
1)  Liquids, debris and precipitation shall not accumulate in the contained space created by the secondary containment.
Liquids, debris and precipitation shall not accumulate in the contained space created by the secondary containment.
 Liquids, debris and precipitation shall not accumulate in the contained space created by the secondary containment.
Liquids, debris and precipitation shall not accumulate in the contained space created by the secondary containment.
2)  Provisions shall be made for removing liquid from the secondary containment in conformance with Subsection 4.1.6.
Provisions shall be made for removing liquid from the secondary containment in conformance with Subsection 4.1.6.
 Provisions shall be made for removing liquid from the secondary containment in conformance with Subsection 4.1.6.
Provisions shall be made for removing liquid from the secondary containment in conformance with Subsection 4.1.6.3)  Controls for the liquid removal system required in Sentence (2) shall be
Controls for the liquid removal system required in Sentence (2) shall be
 Controls for the liquid removal system required in Sentence (2) shall be
Controls for the liquid removal system required in Sentence (2) shall bea) normally closed,
b) accessible under fire exposure conditions, and
c) located so they can be operated from outside the contained space.
4.3.7.9. Use of Secondary Containment
4.3.8. Installation of Underground Storage Tanks
4.3.8.1.  Construction
Construction
1)  Storage tanks installed underground shall be of double-walled construction and shall be built in conformance
with the underground storage tank standards identified in Sentence 4.3.1.2.(1).
Storage tanks installed underground shall be of double-walled construction and shall be built in conformance
with the underground storage tank standards identified in Sentence 4.3.1.2.(1).
 Storage tanks installed underground shall be of double-walled construction and shall be built in conformance
with the underground storage tank standards identified in Sentence 4.3.1.2.(1).
Storage tanks installed underground shall be of double-walled construction and shall be built in conformance
with the underground storage tank standards identified in Sentence 4.3.1.2.(1).
4.3.8.2. Location
1)  Underground storage tanks shall be located so that loads from building foundations and supports are not transmitted to the tank.
Underground storage tanks shall be located so that loads from building foundations and supports are not transmitted to the tank.
 Underground storage tanks shall be located so that loads from building foundations and supports are not transmitted to the tank.
Underground storage tanks shall be located so that loads from building foundations and supports are not transmitted to the tank.
2)  Underground storage tanks shall be separated by a horizontal distance of not less than
Underground storage tanks shall be separated by a horizontal distance of not less than
 Underground storage tanks shall be separated by a horizontal distance of not less than
Underground storage tanks shall be separated by a horizontal distance of not less thana) 600 mm from adjacent underground tanks or structures,
c) 1.5 m from other property lines.
4.3.8.3. Ground Cover
1)  Except as required in Sentences (2) to (4), underground storage tanks shall be installed with not less than 600 mm of ground cover
over the tank.
Except as required in Sentences (2) to (4), underground storage tanks shall be installed with not less than 600 mm of ground cover
over the tank.
 Except as required in Sentences (2) to (4), underground storage tanks shall be installed with not less than 600 mm of ground cover
over the tank.
Except as required in Sentences (2) to (4), underground storage tanks shall be installed with not less than 600 mm of ground cover
over the tank.
2)  Except as required in Sentence (3), storage tanks subjected to vehicular traffic shall be installed not less than 1 m below finished
ground level.
Except as required in Sentence (3), storage tanks subjected to vehicular traffic shall be installed not less than 1 m below finished
ground level.
 Except as required in Sentence (3), storage tanks subjected to vehicular traffic shall be installed not less than 1 m below finished
ground level.
Except as required in Sentence (3), storage tanks subjected to vehicular traffic shall be installed not less than 1 m below finished
ground level.
3)  Either a 150 mm reinforced concrete slab or a 200 mm unreinforced concrete slab over not less than 450 mm of sand is permitted in lieu of the protection described in Sentence (2) provided the slab extends at least 300 mm beyond the storage tank.
Either a 150 mm reinforced concrete slab or a 200 mm unreinforced concrete slab over not less than 450 mm of sand is permitted in lieu of the protection described in Sentence (2) provided the slab extends at least 300 mm beyond the storage tank.
 Either a 150 mm reinforced concrete slab or a 200 mm unreinforced concrete slab over not less than 450 mm of sand is permitted in lieu of the protection described in Sentence (2) provided the slab extends at least 300 mm beyond the storage tank.
Either a 150 mm reinforced concrete slab or a 200 mm unreinforced concrete slab over not less than 450 mm of sand is permitted in lieu of the protection described in Sentence (2) provided the slab extends at least 300 mm beyond the storage tank.
4)  Where subsurface conditions make it impracticable to install a storage tank totally below adjacent ground level, an underground storage tank shall be installed so that at least
Where subsurface conditions make it impracticable to install a storage tank totally below adjacent ground level, an underground storage tank shall be installed so that at least
 Where subsurface conditions make it impracticable to install a storage tank totally below adjacent ground level, an underground storage tank shall be installed so that at least
Where subsurface conditions make it impracticable to install a storage tank totally below adjacent ground level, an underground storage tank shall be installed so that at leasta) 75% of its mass is below adjacent ground level provided there is not less than 600 mm of ground cover over the portion
of the tank above adjacent ground level, or
b) 50% of its mass is below adjacent ground level provided there
is not less than 1 m of ground cover over the portion
of the tank above adjacent ground level.
4.3.8.4. Damage Repair
1)  Underground storage tanks that are in the process of being installed shall be inspected, and any
damage to the tank shell, protective coating, fittings or anodes shall
be repaired before they are lowered into the excavation.
Underground storage tanks that are in the process of being installed shall be inspected, and any
damage to the tank shell, protective coating, fittings or anodes shall
be repaired before they are lowered into the excavation.
 Underground storage tanks that are in the process of being installed shall be inspected, and any
damage to the tank shell, protective coating, fittings or anodes shall
be repaired before they are lowered into the excavation.
Underground storage tanks that are in the process of being installed shall be inspected, and any
damage to the tank shell, protective coating, fittings or anodes shall
be repaired before they are lowered into the excavation.
2)  Damage to storage tank shells shall not be repaired on site.
Damage to storage tank shells shall not be repaired on site.
 Damage to storage tank shells shall not be repaired on site.
Damage to storage tank shells shall not be repaired on site.
4.3.8.5. Damage Prevention
1)  Underground storage tanks shall be lowered into the excavation by the use of lifting lugs and hooks
and, where necessary, spreader bars to prevent damage to the tank
shell, protective coating, fittings or anodes.
Underground storage tanks shall be lowered into the excavation by the use of lifting lugs and hooks
and, where necessary, spreader bars to prevent damage to the tank
shell, protective coating, fittings or anodes.
 Underground storage tanks shall be lowered into the excavation by the use of lifting lugs and hooks
and, where necessary, spreader bars to prevent damage to the tank
shell, protective coating, fittings or anodes.
Underground storage tanks shall be lowered into the excavation by the use of lifting lugs and hooks
and, where necessary, spreader bars to prevent damage to the tank
shell, protective coating, fittings or anodes.
2)  Any method of handling that might result in damage to the protective coating of the tank shall not be used.
Any method of handling that might result in damage to the protective coating of the tank shall not be used.
 Any method of handling that might result in damage to the protective coating of the tank shall not be used.
Any method of handling that might result in damage to the protective coating of the tank shall not be used.
4.3.8.6. Installation
1)  Underground steel storage tanks shall be installed in conformance with Appendix A of CAN/ULC-S603.1, “External Corrosion Protection Systems for Steel Underground Tanks for Flammable and Combustible Liquids.”
Underground steel storage tanks shall be installed in conformance with Appendix A of CAN/ULC-S603.1, “External Corrosion Protection Systems for Steel Underground Tanks for Flammable and Combustible Liquids.”
 Underground steel storage tanks shall be installed in conformance with Appendix A of CAN/ULC-S603.1, “External Corrosion Protection Systems for Steel Underground Tanks for Flammable and Combustible Liquids.”
Underground steel storage tanks shall be installed in conformance with Appendix A of CAN/ULC-S603.1, “External Corrosion Protection Systems for Steel Underground Tanks for Flammable and Combustible Liquids.”2)  Underground reinforced plastic storage tanks shall be installed in conformance with Appendix A of ULC-S615, “Reinforced Plastic Underground Tanks for Flammable and Combustible Liquids.”
Underground reinforced plastic storage tanks shall be installed in conformance with Appendix A of ULC-S615, “Reinforced Plastic Underground Tanks for Flammable and Combustible Liquids.”
 Underground reinforced plastic storage tanks shall be installed in conformance with Appendix A of ULC-S615, “Reinforced Plastic Underground Tanks for Flammable and Combustible Liquids.”
Underground reinforced plastic storage tanks shall be installed in conformance with Appendix A of ULC-S615, “Reinforced Plastic Underground Tanks for Flammable and Combustible Liquids.”3)  Underground storage tanks shall not be placed in direct contact with reinforced concrete slabs but
shall be separated by not less than 150 mm of sand or
other suitable material to evenly distribute the weight of the tank
on the supporting base.
Underground storage tanks shall not be placed in direct contact with reinforced concrete slabs but
shall be separated by not less than 150 mm of sand or
other suitable material to evenly distribute the weight of the tank
on the supporting base.
 Underground storage tanks shall not be placed in direct contact with reinforced concrete slabs but
shall be separated by not less than 150 mm of sand or
other suitable material to evenly distribute the weight of the tank
on the supporting base.
Underground storage tanks shall not be placed in direct contact with reinforced concrete slabs but
shall be separated by not less than 150 mm of sand or
other suitable material to evenly distribute the weight of the tank
on the supporting base.
4.3.8.7. Filling
1)  Flammable liquids or combustible liquids shall not be placed in an underground storage tank until
Flammable liquids or combustible liquids shall not be placed in an underground storage tank until
 Flammable liquids or combustible liquids shall not be placed in an underground storage tank until
Flammable liquids or combustible liquids shall not be placed in an underground storage tank untila) the fill pipe and vent line have been installed in the tank, and
b) all other openings have been sealed.
4.3.8.8. Spillage
1)  If a spillage occurs, the escaped liquid and all soil contaminated by the spill shall be removed in conformance with Subsection 4.1.6.
If a spillage occurs, the escaped liquid and all soil contaminated by the spill shall be removed in conformance with Subsection 4.1.6.
 If a spillage occurs, the escaped liquid and all soil contaminated by the spill shall be removed in conformance with Subsection 4.1.6.
If a spillage occurs, the escaped liquid and all soil contaminated by the spill shall be removed in conformance with Subsection 4.1.6.4.3.8.9. Anchorage
1)  Underground storage tanks shall be protected against hydrostatic forces which can cause the uplift
of the tanks once they are empty. (See Appendix A.)
Underground storage tanks shall be protected against hydrostatic forces which can cause the uplift
of the tanks once they are empty. (See Appendix A.)
 Underground storage tanks shall be protected against hydrostatic forces which can cause the uplift
of the tanks once they are empty. (See Appendix A.)
Underground storage tanks shall be protected against hydrostatic forces which can cause the uplift
of the tanks once they are empty. (See Appendix A.) 2)  Where anchors and ground straps are used to resist the uplift forces referred to in Sentence (1), they shall be
Where anchors and ground straps are used to resist the uplift forces referred to in Sentence (1), they shall be
 Where anchors and ground straps are used to resist the uplift forces referred to in Sentence (1), they shall be
Where anchors and ground straps are used to resist the uplift forces referred to in Sentence (1), they shall bea) electrically isolated from the tank, and
b) installed in such a manner that they do not damage the tank's
shell, protective coating, fittings or anodes.
4.3.9. Sumps
4.3.9.1.  Installation
Installation
1)  A dispenser sump shall be provided under a dispenser, unless the dispenser is located on top of an aboveground storage tank.
A dispenser sump shall be provided under a dispenser, unless the dispenser is located on top of an aboveground storage tank.
 A dispenser sump shall be provided under a dispenser, unless the dispenser is located on top of an aboveground storage tank.
A dispenser sump shall be provided under a dispenser, unless the dispenser is located on top of an aboveground storage tank. 4)  A turbine sump shall be provided for all turbine pump assemblies located below grade or above grade where they are not readily visible.
A turbine sump shall be provided for all turbine pump assemblies located below grade or above grade where they are not readily visible.
 A turbine sump shall be provided for all turbine pump assemblies located below grade or above grade where they are not readily visible.
A turbine sump shall be provided for all turbine pump assemblies located below grade or above grade where they are not readily visible.
5) In addition to the requirements of  Article 4.3.9.2.
Article 4.3.9.2. , the sumps referred to in Sentences (1) to (4) shall be installed in conformance with the sump manufacturer’s instructions.
, the sumps referred to in Sentences (1) to (4) shall be installed in conformance with the sump manufacturer’s instructions.
 Article 4.3.9.2.
Article 4.3.9.2. , the sumps referred to in Sentences (1) to (4) shall be installed in conformance with the sump manufacturer’s instructions.
, the sumps referred to in Sentences (1) to (4) shall be installed in conformance with the sump manufacturer’s instructions.

4.3.9.2.  Construction
Construction
1) Dispenser sumps shall conform to the construction and performance requirements of ULC/ORD-C107.21, “Under-Dispenser Sumps.”
2) Spill containment sumps shall canfaIDl to the construction and performance requirements of ULC/ORD-C58.19, “Spill Containment Devices for Underground Flammable
Liquid Storage Tanks.”
4.3.9.3. Leak Detection Monitoring
1) Where dispenser sumps, turbine sumps and transition sumps referred to in Article 4.3.9.1. are used in underground applications, they shall be provided with an electronic monitoring device to indicate the presence of liquid.

4.3.10. Corrosion Protection of Underground Steel Storage Tanks
4.3.10.1. Corrosion Protection
1)  Underground steel storage tanks and
Underground steel storage tanks and  integral fittings
integral fittings subject to corrosion shall be
subject to corrosion shall be
 Underground steel storage tanks and
Underground steel storage tanks and  integral fittings
integral fittings subject to corrosion shall be
subject to corrosion shall bea) protected in conformance with CAN/ULC-S603.1, “External Corrosion Protection Systems for Steel Underground Tanks for Flammable and Combustible Liquids,” or
b)  protected by impressed current in conformance with NACE RP0285, “Corrosion Control of Underground Storage Tank Systems by Cathodic Protection.”
protected by impressed current in conformance with NACE RP0285, “Corrosion Control of Underground Storage Tank Systems by Cathodic Protection.”
 protected by impressed current in conformance with NACE RP0285, “Corrosion Control of Underground Storage Tank Systems by Cathodic Protection.”
protected by impressed current in conformance with NACE RP0285, “Corrosion Control of Underground Storage Tank Systems by Cathodic Protection.”
4.3.10.2.  BC Deletion
BC Deletion

4.3.10.3.  BC Deletion
BC Deletion

4.3.11. Vents for Underground Storage Tanks
4.3.11.1. Vent Design
1)  Underground storage tanks shall be provided with vent openings and piping of sufficient cross-sectional
area designed to vent the tanks during the maximum filling or withdrawal
rate without causing the allowable stress for the tank to be exceeded.
Underground storage tanks shall be provided with vent openings and piping of sufficient cross-sectional
area designed to vent the tanks during the maximum filling or withdrawal
rate without causing the allowable stress for the tank to be exceeded.
 Underground storage tanks shall be provided with vent openings and piping of sufficient cross-sectional
area designed to vent the tanks during the maximum filling or withdrawal
rate without causing the allowable stress for the tank to be exceeded.
Underground storage tanks shall be provided with vent openings and piping of sufficient cross-sectional
area designed to vent the tanks during the maximum filling or withdrawal
rate without causing the allowable stress for the tank to be exceeded.
4.3.11.2. Materials and Construction
1)  Except at distilleries covered in Section 4.10., vent piping materials and construction shall conform to Subsections 4.5.2., 4.5.3. and 4.5.5.
Except at distilleries covered in Section 4.10., vent piping materials and construction shall conform to Subsections 4.5.2., 4.5.3. and 4.5.5.
 Except at distilleries covered in Section 4.10., vent piping materials and construction shall conform to Subsections 4.5.2., 4.5.3. and 4.5.5.
Except at distilleries covered in Section 4.10., vent piping materials and construction shall conform to Subsections 4.5.2., 4.5.3. and 4.5.5.4.3.11.3. Installation
1)  Vent pipe outlets from underground storage tanks for Class I liquids
Vent pipe outlets from underground storage tanks for Class I liquids
 Vent pipe outlets from underground storage tanks for Class I liquids
Vent pipe outlets from underground storage tanks for Class I liquidsa) shall be located outside buildings higher than the fill pipe openings but not less than
i) 3.5 m above the adjacent ground level,
ii) 1.5 m from any building opening, and
iii) 7.5 m from any dispenser, and
2)  Vent pipe outlets from underground storage tanks for Class II or IIIA liquids shall be located outside buildings at a height that is above the fill pipe opening but not less than 2 m above finished ground
level.
Vent pipe outlets from underground storage tanks for Class II or IIIA liquids shall be located outside buildings at a height that is above the fill pipe opening but not less than 2 m above finished ground
level.
 Vent pipe outlets from underground storage tanks for Class II or IIIA liquids shall be located outside buildings at a height that is above the fill pipe opening but not less than 2 m above finished ground
level.
Vent pipe outlets from underground storage tanks for Class II or IIIA liquids shall be located outside buildings at a height that is above the fill pipe opening but not less than 2 m above finished ground
level.
3)  Vent pipes from underground storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids shall not be obstructed by any device that may cause excessive back pressure, except that
vent pipes from underground storage tanks for Class II or IIIA liquids are permitted to be fitted with return bends, coarse screens or other devices to minimize the entry of foreign
material.
Vent pipes from underground storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids shall not be obstructed by any device that may cause excessive back pressure, except that
vent pipes from underground storage tanks for Class II or IIIA liquids are permitted to be fitted with return bends, coarse screens or other devices to minimize the entry of foreign
material.
 Vent pipes from underground storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids shall not be obstructed by any device that may cause excessive back pressure, except that
vent pipes from underground storage tanks for Class II or IIIA liquids are permitted to be fitted with return bends, coarse screens or other devices to minimize the entry of foreign
material.
Vent pipes from underground storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids shall not be obstructed by any device that may cause excessive back pressure, except that
vent pipes from underground storage tanks for Class II or IIIA liquids are permitted to be fitted with return bends, coarse screens or other devices to minimize the entry of foreign
material.
4)  Vent piping shall enter the storage tank through the top of the tank and shall not extend into the tank more than 25 mm.
Vent piping shall enter the storage tank through the top of the tank and shall not extend into the tank more than 25 mm.
 Vent piping shall enter the storage tank through the top of the tank and shall not extend into the tank more than 25 mm.
Vent piping shall enter the storage tank through the top of the tank and shall not extend into the tank more than 25 mm.
5)  Vent piping shall be
Vent piping shall be
 Vent piping shall be
Vent piping shall bea) installed so that any nominally horizontal run shall slope towards the storage tank,
b) constructed without traps,
c) adequately supported to prevent sagging, and
d) where necessary, protected against mechanical damage.
6) 
 Vent piping shall be tested for leaks at the commissioning stage in conformance with Clause 4.4.1.2.(1)(a).
Vent piping shall be tested for leaks at the commissioning stage in conformance with Clause 4.4.1.2.(1)(a).

 Vent piping shall be tested for leaks at the commissioning stage in conformance with Clause 4.4.1.2.(1)(a).
Vent piping shall be tested for leaks at the commissioning stage in conformance with Clause 4.4.1.2.(1)(a).
4.3.11.4. Interconnection of Vent Pipes
1)  Except as permitted in Sentence (2), where vent piping connects 2 or more storage tanks, pipe sizes shall be designed to vent the combined vapours
produced in the connected underground storage tanks without exceeding the allowable stresses of the tanks
when being filled simultaneously.
Except as permitted in Sentence (2), where vent piping connects 2 or more storage tanks, pipe sizes shall be designed to vent the combined vapours
produced in the connected underground storage tanks without exceeding the allowable stresses of the tanks
when being filled simultaneously.
 Except as permitted in Sentence (2), where vent piping connects 2 or more storage tanks, pipe sizes shall be designed to vent the combined vapours
produced in the connected underground storage tanks without exceeding the allowable stresses of the tanks
when being filled simultaneously.
Except as permitted in Sentence (2), where vent piping connects 2 or more storage tanks, pipe sizes shall be designed to vent the combined vapours
produced in the connected underground storage tanks without exceeding the allowable stresses of the tanks
when being filled simultaneously.
2)  Where it is not possible to fill the connected storage tanks referred to in Sentence (1) simultaneously, or where the connected vents have a vapour recovery system, the vent piping shall be sized
to accommodate the maximum vapour flow possible in the system.
Where it is not possible to fill the connected storage tanks referred to in Sentence (1) simultaneously, or where the connected vents have a vapour recovery system, the vent piping shall be sized
to accommodate the maximum vapour flow possible in the system.
 Where it is not possible to fill the connected storage tanks referred to in Sentence (1) simultaneously, or where the connected vents have a vapour recovery system, the vent piping shall be sized
to accommodate the maximum vapour flow possible in the system.
Where it is not possible to fill the connected storage tanks referred to in Sentence (1) simultaneously, or where the connected vents have a vapour recovery system, the vent piping shall be sized
to accommodate the maximum vapour flow possible in the system.
3)  Vent piping for an underground storage tank containing a Class I liquid shall not be connected to
the vent piping for a storage tank containing a Class II or IIIA liquid unless an effective method is provided to
prevent the vapours from the Class I liquid storage tank from entering the other tank.
Vent piping for an underground storage tank containing a Class I liquid shall not be connected to
the vent piping for a storage tank containing a Class II or IIIA liquid unless an effective method is provided to
prevent the vapours from the Class I liquid storage tank from entering the other tank.
 Vent piping for an underground storage tank containing a Class I liquid shall not be connected to
the vent piping for a storage tank containing a Class II or IIIA liquid unless an effective method is provided to
prevent the vapours from the Class I liquid storage tank from entering the other tank.
Vent piping for an underground storage tank containing a Class I liquid shall not be connected to
the vent piping for a storage tank containing a Class II or IIIA liquid unless an effective method is provided to
prevent the vapours from the Class I liquid storage tank from entering the other tank. 4.3.12. Openings Other than Vents in Underground Storage Tanks
4.3.12.1. Connections
1)  Connections for all openings in underground storage tanks shall be liquid- and vapour-tight.
Connections for all openings in underground storage tanks shall be liquid- and vapour-tight.
 Connections for all openings in underground storage tanks shall be liquid- and vapour-tight.
Connections for all openings in underground storage tanks shall be liquid- and vapour-tight. 4.3.12.2. Openings for Measuring Liquid Level
1)  Openings for measuring liquid levels in underground storage tanks if independent of the fill pipe shall be equipped with a vapour-tight cap or cover which shall be
opened only when measuring the liquid level.
Openings for measuring liquid levels in underground storage tanks if independent of the fill pipe shall be equipped with a vapour-tight cap or cover which shall be
opened only when measuring the liquid level.
 Openings for measuring liquid levels in underground storage tanks if independent of the fill pipe shall be equipped with a vapour-tight cap or cover which shall be
opened only when measuring the liquid level.
Openings for measuring liquid levels in underground storage tanks if independent of the fill pipe shall be equipped with a vapour-tight cap or cover which shall be
opened only when measuring the liquid level.
4.3.12.3. Fill Piping and Discharge Piping
1)  Fill piping and discharge piping shall enter underground storage tanks only through the top of the tank and discharge piping used in suction systems shall be sloped toward
the storage tanks.
Fill piping and discharge piping shall enter underground storage tanks only through the top of the tank and discharge piping used in suction systems shall be sloped toward
the storage tanks.
 Fill piping and discharge piping shall enter underground storage tanks only through the top of the tank and discharge piping used in suction systems shall be sloped toward
the storage tanks.
Fill piping and discharge piping shall enter underground storage tanks only through the top of the tank and discharge piping used in suction systems shall be sloped toward
the storage tanks. 2) 
 The fill point of an underground storage tank shall not be located higher than the discharge point of the tank’s vent.
The fill point of an underground storage tank shall not be located higher than the discharge point of the tank’s vent.

 The fill point of an underground storage tank shall not be located higher than the discharge point of the tank’s vent.
The fill point of an underground storage tank shall not be located higher than the discharge point of the tank’s vent.
3)  Except as provided in Sentence (5), connections used as part of normal operating conditions for filling or emptying storage tanks for flammable liquids and combustible liquids shall be located
Except as provided in Sentence (5), connections used as part of normal operating conditions for filling or emptying storage tanks for flammable liquids and combustible liquids shall be located
 Except as provided in Sentence (5), connections used as part of normal operating conditions for filling or emptying storage tanks for flammable liquids and combustible liquids shall be located
Except as provided in Sentence (5), connections used as part of normal operating conditions for filling or emptying storage tanks for flammable liquids and combustible liquids shall be locateda) outside buildings,
b) at a location free of sources of ignition, and
c) not less than 1.5 m away from building openings.
4)  Connections for filling or emptying storage tanks described in Sentence (3) shall be kept closed to prevent leakage when not in use.
Connections for filling or emptying storage tanks described in Sentence (3) shall be kept closed to prevent leakage when not in use.
 Connections for filling or emptying storage tanks described in Sentence (3) shall be kept closed to prevent leakage when not in use.
Connections for filling or emptying storage tanks described in Sentence (3) shall be kept closed to prevent leakage when not in use.
5)  A filling connection described in Sentence (3) is permitted to be located inside a building if
A filling connection described in Sentence (3) is permitted to be located inside a building if
 A filling connection described in Sentence (3) is permitted to be located inside a building if
A filling connection described in Sentence (3) is permitted to be located inside a building ifa) this is made necessary
i) by a process or activity located indoors and to which the storage tank is directly associated, or
ii) for the collection of used liquids, and
b) the fill piping is provided with means to prevent flammable
vapours from returning to the building.
6) 
 If a fill piping system has an offset component from the fill point on the storage tank, all fill pipes shall be
If a fill piping system has an offset component from the fill point on the storage tank, all fill pipes shall be

 If a fill piping system has an offset component from the fill point on the storage tank, all fill pipes shall be
If a fill piping system has an offset component from the fill point on the storage tank, all fill pipes shall bea) double-walled,
b) sloped to the storage tank, and
c) electronically monitored for leak detection in conformance with Section 4.4.
(See Appendix A.)7)  Where the fill point is below the normal liquid level in the storage tank,
Where the fill point is below the normal liquid level in the storage tank,
 Where the fill point is below the normal liquid level in the storage tank,
Where the fill point is below the normal liquid level in the storage tank,a) the fill line shall be equipped with a manual or automatic valve located at the fill point to prevent spillage when the fill cap is
removed, and
b) if the storage tank contains flammable liquids or combustible liquids, the fill line drop tube shall be equipped with a method to prevent siphoning of the tank's content should a
leak occur in the fill line.

4.3.13. Installation of Storage Tanks inside Buildings
4.3.13.1. Occupancy
1)  Except as provided in Article 4.3.13.2., storage tanks inside buildings shall
Except as provided in Article 4.3.13.2., storage tanks inside buildings shall
 Except as provided in Article 4.3.13.2., storage tanks inside buildings shall
Except as provided in Article 4.3.13.2., storage tanks inside buildings shalla) conform to Subsections 4.3.13. to 4.3.15.,
b) be permitted in industrial occupancies, and
c)  be permitted in all occupancies where combustible liquids are stored and used as fuel for oil-burning equipment, emergency generators and fire
pumps.
be permitted in all occupancies where combustible liquids are stored and used as fuel for oil-burning equipment, emergency generators and fire
pumps.
 be permitted in all occupancies where combustible liquids are stored and used as fuel for oil-burning equipment, emergency generators and fire
pumps.
be permitted in all occupancies where combustible liquids are stored and used as fuel for oil-burning equipment, emergency generators and fire
pumps.
4.3.13.2. Stationary Combustion Engines
1)  Installations using Class I liquids as fuel supplies for stationary engines inside buildings shall conform to NFPA 37, “Installation and Use of Stationary Combustion Engines and Gas Turbines.”
Installations using Class I liquids as fuel supplies for stationary engines inside buildings shall conform to NFPA 37, “Installation and Use of Stationary Combustion Engines and Gas Turbines.”
 Installations using Class I liquids as fuel supplies for stationary engines inside buildings shall conform to NFPA 37, “Installation and Use of Stationary Combustion Engines and Gas Turbines.”
Installations using Class I liquids as fuel supplies for stationary engines inside buildings shall conform to NFPA 37, “Installation and Use of Stationary Combustion Engines and Gas Turbines.”4.3.13.3. Maximum Static Head
1)  The static head imposed on a storage tank inside a building shall not exceed 70 kPa (gauge) at the bottom of the tank when the vent or fill pipe is filled with liquid unless the tank is designed for greater
pressures.
The static head imposed on a storage tank inside a building shall not exceed 70 kPa (gauge) at the bottom of the tank when the vent or fill pipe is filled with liquid unless the tank is designed for greater
pressures.
 The static head imposed on a storage tank inside a building shall not exceed 70 kPa (gauge) at the bottom of the tank when the vent or fill pipe is filled with liquid unless the tank is designed for greater
pressures.
The static head imposed on a storage tank inside a building shall not exceed 70 kPa (gauge) at the bottom of the tank when the vent or fill pipe is filled with liquid unless the tank is designed for greater
pressures.
4.3.13.4. Maximum Quantities and Location
1)  Except as provided in Subsection 4.2.8. and in Sentence (2), storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids shall be
Except as provided in Subsection 4.2.8. and in Sentence (2), storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids shall be
 Except as provided in Subsection 4.2.8. and in Sentence (2), storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids shall be
Except as provided in Subsection 4.2.8. and in Sentence (2), storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids shall bea) located in dedicated storage rooms conforming to Subsection 4.3.14., and
2)  When quantities greater than those permitted for incidental use in Subsection 4.2.8. are required for special process
operations, storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids are permitted to be located outside of a storage room referred to in Sentence (1), provided that
When quantities greater than those permitted for incidental use in Subsection 4.2.8. are required for special process
operations, storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids are permitted to be located outside of a storage room referred to in Sentence (1), provided that
 When quantities greater than those permitted for incidental use in Subsection 4.2.8. are required for special process
operations, storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids are permitted to be located outside of a storage room referred to in Sentence (1), provided that
When quantities greater than those permitted for incidental use in Subsection 4.2.8. are required for special process
operations, storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids are permitted to be located outside of a storage room referred to in Sentence (1), provided thata) total quantities per fire compartment are not more than one-half the quantities permitted in Table 4.3.13.4.A,
b) they are located on the first storey, and
| Table 4.3.13.4.A Indoor Tank Storage  in Industrial Occupancies in Industrial Occupancies Forming part of Sentences 4.3.13.4.(1) and (2), and 4.3.13.8.(1) | |||
| Class of Liquid | Storage Level |
Maximum Quantity per Storage Room(1), L |
|
| One or More Tanks | |||
|
Protected Storage(2) | Unprotected Storage | ||
|
Class I |
40 000 | 25 000 | |
|
Storeys above the first storey |
7 500 | Not Permitted | |
| Not Permitted | Not Permitted | ||
|
Classes II and IIIA |
200 000 | 100 000 | |
|
Storeys above the first storey |
20 000 | Not Permitted | |
| 20 000 | Not Permitted | ||
| Notes to Table 4.3.13.4.A: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | See Subsection 4.3.14. |
| (2) | See Article 4.2.7.6. |
Table 4.3.13.4.B Indoor Tank Storage in Occupancies Using Oil-Burning Equipment, Emergency Generators and Fire Pumps Indoor Tank Storage in Occupancies Using Oil-Burning Equipment, Emergency Generators and Fire PumpsForming part of Sentences 4.3.13.4.(1) and 4.3.13.5.(1) and (2) | |||
| Class of Liquid | Storage Level |
Quantity per Protected Storage Room(1), L |
|
|
Individual Tank |
Aggregate | ||
|
Classes II and IIIA |
> 2 500(2)(3) | 200 000 | |
| > 20 000(2)(4) | |||
|
Basement and storeys above the first storey |
> 2 500(3) | 20 000 | |
| > 20 000(4) | 45 000 | ||
| Notes to Table 4.3.13.4.B: | |
|
|
|
| (1) | See Article 4.2.7.6. |
| (2) | For industrial occupancies where the tanks are located in a separate storage room from the equipment, refer to Table 4.3.13.4.A. |
| (3) | See Sentence 4.3.13.5.(1). |
| (4) | See Sentence 4.3.13.5.(2). |
4.3.13.5. Storage Tank Construction
1)  Storage tanks with an individual capacity exceeding 2 500 L but not exceeding 20 000
L that are used in conformance with Table 4.3.13.4.B shall be
Storage tanks with an individual capacity exceeding 2 500 L but not exceeding 20 000
L that are used in conformance with Table 4.3.13.4.B shall be
 Storage tanks with an individual capacity exceeding 2 500 L but not exceeding 20 000
L that are used in conformance with Table 4.3.13.4.B shall be
Storage tanks with an individual capacity exceeding 2 500 L but not exceeding 20 000
L that are used in conformance with Table 4.3.13.4.B shall bea) of double-walled construction in conformance with Clause 4.3.1.2.(1)(e) or a minimum of 300 deg. secondarily contained construction, and
b) monitored for leakage in conformance with Sentence 4.4.2.1.(7).
2)  Storage tanks with an individual capacity exceeding 20 000 L that are used in conformance
with Table 4.3.13.4.B shall
Storage tanks with an individual capacity exceeding 20 000 L that are used in conformance
with Table 4.3.13.4.B shall
 Storage tanks with an individual capacity exceeding 20 000 L that are used in conformance
with Table 4.3.13.4.B shall
Storage tanks with an individual capacity exceeding 20 000 L that are used in conformance
with Table 4.3.13.4.B shalla) conform to Clause 4.3.1.2.(1)(l), and
b) be monitored for leakage in conformance with Sentence 4.4.2.1.(7).
4.3.13.6. Piping Systems
1)  Piping systems serving oil-burning equipment, diesel-engine-driven emergency generators and fire pumps shall conform to CSA B139, “Installation Code for Oil-Burning Equipment.”
Piping systems serving oil-burning equipment, diesel-engine-driven emergency generators and fire pumps shall conform to CSA B139, “Installation Code for Oil-Burning Equipment.”
 Piping systems serving oil-burning equipment, diesel-engine-driven emergency generators and fire pumps shall conform to CSA B139, “Installation Code for Oil-Burning Equipment.”
Piping systems serving oil-burning equipment, diesel-engine-driven emergency generators and fire pumps shall conform to CSA B139, “Installation Code for Oil-Burning Equipment.”
4.3.13.7. Fire Compartments
1)  Fire compartments regulated by this Subsection shall be separated from the remainder of the building by a fire separation having a fire-resistance rating of not less than 2 h.
Fire compartments regulated by this Subsection shall be separated from the remainder of the building by a fire separation having a fire-resistance rating of not less than 2 h.
 Fire compartments regulated by this Subsection shall be separated from the remainder of the building by a fire separation having a fire-resistance rating of not less than 2 h.
Fire compartments regulated by this Subsection shall be separated from the remainder of the building by a fire separation having a fire-resistance rating of not less than 2 h.
4.3.13.8. Mixed Storage
1)  When 2 or more classes of liquids are stored in a single storage room referred to in Sentence 4.3.13.4.(1), the total quantity permitted for each class of liquid shall be calculated as follows:
When 2 or more classes of liquids are stored in a single storage room referred to in Sentence 4.3.13.4.(1), the total quantity permitted for each class of liquid shall be calculated as follows:
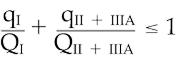 where
where
 When 2 or more classes of liquids are stored in a single storage room referred to in Sentence 4.3.13.4.(1), the total quantity permitted for each class of liquid shall be calculated as follows:
When 2 or more classes of liquids are stored in a single storage room referred to in Sentence 4.3.13.4.(1), the total quantity permitted for each class of liquid shall be calculated as follows:
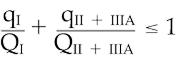
qI= the actual quantity of Class I liquids present,
qII + IIIA= the actual quantity of Class II and IIIA liquids
present,
QI= the maximum quantity of Class I liquids permitted in Table 4.3.13.4.A,
QII + IIIA= the maximum quantity of Class II and IIIA liquids permitted in
Table 4.3.13.4.A.
4.3.13.9. Storage Tanks outside Storage Rooms
1)  Where storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids are located outside of storage rooms conforming to Subsection 4.3.14.,
Where storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids are located outside of storage rooms conforming to Subsection 4.3.14.,
 Where storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids are located outside of storage rooms conforming to Subsection 4.3.14.,
Where storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids are located outside of storage rooms conforming to Subsection 4.3.14.,a) provision shall be made to contain  a spill equal to at least
a spill equal to at least 100% of the volume of the largest storage tank, or to drain away spilled flammable liquids or combustible liquids, and
100% of the volume of the largest storage tank, or to drain away spilled flammable liquids or combustible liquids, and
 a spill equal to at least
a spill equal to at least 100% of the volume of the largest storage tank, or to drain away spilled flammable liquids or combustible liquids, and
100% of the volume of the largest storage tank, or to drain away spilled flammable liquids or combustible liquids, and b) the area in which the storage tanks are located shall be ventilated (see Appendix A).
4.3.13.10. Vents
1)  Except as provided in Sentence (2), normal and emergency vents for storage tanks in buildings shall be provided in conformance with Subsections 4.3.4. and 4.3.5. (See Appendix A.)
Except as provided in Sentence (2), normal and emergency vents for storage tanks in buildings shall be provided in conformance with Subsections 4.3.4. and 4.3.5. (See Appendix A.)
 Except as provided in Sentence (2), normal and emergency vents for storage tanks in buildings shall be provided in conformance with Subsections 4.3.4. and 4.3.5. (See Appendix A.)
Except as provided in Sentence (2), normal and emergency vents for storage tanks in buildings shall be provided in conformance with Subsections 4.3.4. and 4.3.5. (See Appendix A.) 2)  The use of weak roof-to-side shell seams, designed to rupture before the allowable design stress of the storage tank is reached, shall not be permitted as a means of emergency
venting of storage tanks inside buildings.
The use of weak roof-to-side shell seams, designed to rupture before the allowable design stress of the storage tank is reached, shall not be permitted as a means of emergency
venting of storage tanks inside buildings.
 The use of weak roof-to-side shell seams, designed to rupture before the allowable design stress of the storage tank is reached, shall not be permitted as a means of emergency
venting of storage tanks inside buildings.
The use of weak roof-to-side shell seams, designed to rupture before the allowable design stress of the storage tank is reached, shall not be permitted as a means of emergency
venting of storage tanks inside buildings. 4.3.13.11. Supports, Foundations and Anchorage
1)  Except as provided in Sentence (2), where storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids are installed inside buildings, the supports, foundations and anchorage for such storage tanks shall be in conformance with Subsection 4.3.3.
Except as provided in Sentence (2), where storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids are installed inside buildings, the supports, foundations and anchorage for such storage tanks shall be in conformance with Subsection 4.3.3.
 Except as provided in Sentence (2), where storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids are installed inside buildings, the supports, foundations and anchorage for such storage tanks shall be in conformance with Subsection 4.3.3.
Except as provided in Sentence (2), where storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids are installed inside buildings, the supports, foundations and anchorage for such storage tanks shall be in conformance with Subsection 4.3.3.2)  Where a storage tank is suspended, rather than supported on a foundation, supports shall be designed
and installed in conformance with good engineering practice. (See Appendix A.)
Where a storage tank is suspended, rather than supported on a foundation, supports shall be designed
and installed in conformance with good engineering practice. (See Appendix A.)
 Where a storage tank is suspended, rather than supported on a foundation, supports shall be designed
and installed in conformance with good engineering practice. (See Appendix A.)
Where a storage tank is suspended, rather than supported on a foundation, supports shall be designed
and installed in conformance with good engineering practice. (See Appendix A.) 4.3.13.12. Bonding and Grounding
1)  Where storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids are installed inside buildings, tanks, piping and discharge equipment shall be bonded and grounded.
Where storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids are installed inside buildings, tanks, piping and discharge equipment shall be bonded and grounded.
 Where storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids are installed inside buildings, tanks, piping and discharge equipment shall be bonded and grounded.
Where storage tanks for flammable liquids or combustible liquids are installed inside buildings, tanks, piping and discharge equipment shall be bonded and grounded.
4.3.14. Rooms for Storage Tanks
4.3.14.1. Design and Construction
1)  Rooms for storage tanks inside buildings, referred to in Sentence 4.3.13.4.(1), shall be
Rooms for storage tanks inside buildings, referred to in Sentence 4.3.13.4.(1), shall be
 Rooms for storage tanks inside buildings, referred to in Sentence 4.3.13.4.(1), shall be
Rooms for storage tanks inside buildings, referred to in Sentence 4.3.13.4.(1), shall bea) separated from the rest of the building by a fire separation having a fire-resistance rating of at least 2 h,
b) designed to contain  a spill equal to at least
a spill equal to at least 100% of the volume of the largest storage tank, or to drain away spilled flammable liquids or combustible liquids,
100% of the volume of the largest storage tank, or to drain away spilled flammable liquids or combustible liquids,
 a spill equal to at least
a spill equal to at least 100% of the volume of the largest storage tank, or to drain away spilled flammable liquids or combustible liquids,
100% of the volume of the largest storage tank, or to drain away spilled flammable liquids or combustible liquids, c) made liquid-tight where the walls join the floor, and
d) used for no other purposes than the storage and handling of flammable liquids or combustible liquids.
4.3.14.2. Clearances
1)  A minimum clear space of 550 mm shall be maintained between the walls of a room described in Article 4.3.14.1. and the sides of any storage tanks within the room.
A minimum clear space of 550 mm shall be maintained between the walls of a room described in Article 4.3.14.1. and the sides of any storage tanks within the room.
 A minimum clear space of 550 mm shall be maintained between the walls of a room described in Article 4.3.14.1. and the sides of any storage tanks within the room.
A minimum clear space of 550 mm shall be maintained between the walls of a room described in Article 4.3.14.1. and the sides of any storage tanks within the room. 4.3.14.3. Explosion Venting
1)  Where Class IA or IB liquids are dispensed within a storage room, the room shall be designed to prevent critical structural and
mechanical damage from an internal explosion in conformance with NFPA 68, “Explosion Protection by Deflagration Venting.” (See A-3.2.8.2.(1)(d) in Appendix A.)
Where Class IA or IB liquids are dispensed within a storage room, the room shall be designed to prevent critical structural and
mechanical damage from an internal explosion in conformance with NFPA 68, “Explosion Protection by Deflagration Venting.” (See A-3.2.8.2.(1)(d) in Appendix A.)
 Where Class IA or IB liquids are dispensed within a storage room, the room shall be designed to prevent critical structural and
mechanical damage from an internal explosion in conformance with NFPA 68, “Explosion Protection by Deflagration Venting.” (See A-3.2.8.2.(1)(d) in Appendix A.)
Where Class IA or IB liquids are dispensed within a storage room, the room shall be designed to prevent critical structural and
mechanical damage from an internal explosion in conformance with NFPA 68, “Explosion Protection by Deflagration Venting.” (See A-3.2.8.2.(1)(d) in Appendix A.) 4.3.14.4. Hose Stations and Portable Extinguishers
1) In buildings not required to be equipped with a standpipe and hose system by the British Columbia Building Code, hose stations shall
be provided in the
vicinity of the storage room, such that all parts of the room are within reach of
a
hose stream. (See Appendix A.)

2)  Portable extinguishers for Class B fires shall be provided.
Portable extinguishers for Class B fires shall be provided.
 Portable extinguishers for Class B fires shall be provided.
Portable extinguishers for Class B fires shall be provided. 4.3.14.5. Placards
1)  Placards conforming to Article 3.2.7.14., identifying the liquids stored as flammable liquids or combustible liquids and the capacities of the storage tanks, shall be posted in a conspicuous location outside of the room, and that information
shall be included in the fire safety plan required in Article 4.1.5.5.
Placards conforming to Article 3.2.7.14., identifying the liquids stored as flammable liquids or combustible liquids and the capacities of the storage tanks, shall be posted in a conspicuous location outside of the room, and that information
shall be included in the fire safety plan required in Article 4.1.5.5.
 Placards conforming to Article 3.2.7.14., identifying the liquids stored as flammable liquids or combustible liquids and the capacities of the storage tanks, shall be posted in a conspicuous location outside of the room, and that information
shall be included in the fire safety plan required in Article 4.1.5.5.
Placards conforming to Article 3.2.7.14., identifying the liquids stored as flammable liquids or combustible liquids and the capacities of the storage tanks, shall be posted in a conspicuous location outside of the room, and that information
shall be included in the fire safety plan required in Article 4.1.5.5.4.3.15. Openings Other than Vents in Storage Tanks inside Buildings
4.3.15.1. Connections
2)  Connections to storage tanks through which liquid can flow shall be provided with valves located as close
as practicable to the tank.
Connections to storage tanks through which liquid can flow shall be provided with valves located as close
as practicable to the tank.
 Connections to storage tanks through which liquid can flow shall be provided with valves located as close
as practicable to the tank.
Connections to storage tanks through which liquid can flow shall be provided with valves located as close
as practicable to the tank.
4.3.15.2. Openings for Liquid Level Measurement
1)  Openings that are independent of the fill pipe and are used for measuring the liquid level in storage tanks containing Class I or II liquids shall be equipped with a vapour-tight cap which shall be opened only when measuring the liquid level.
Openings that are independent of the fill pipe and are used for measuring the liquid level in storage tanks containing Class I or II liquids shall be equipped with a vapour-tight cap which shall be opened only when measuring the liquid level.
 Openings that are independent of the fill pipe and are used for measuring the liquid level in storage tanks containing Class I or II liquids shall be equipped with a vapour-tight cap which shall be opened only when measuring the liquid level.
Openings that are independent of the fill pipe and are used for measuring the liquid level in storage tanks containing Class I or II liquids shall be equipped with a vapour-tight cap which shall be opened only when measuring the liquid level.
2)  Openings referred to in Sentence (1) shall be protected against overflow and vapour pressure by means of a spring-loaded check valve.
Openings referred to in Sentence (1) shall be protected against overflow and vapour pressure by means of a spring-loaded check valve.
 Openings referred to in Sentence (1) shall be protected against overflow and vapour pressure by means of a spring-loaded check valve.
Openings referred to in Sentence (1) shall be protected against overflow and vapour pressure by means of a spring-loaded check valve.
4.3.16. Out of Service
4.3.16.1. Underground Storage Tanks
1)  The removal, abandonment in place, disposal or temporary taking out of service of an underground storage tank shall be in conformance with good engineering practice. (See Appendix A.)
The removal, abandonment in place, disposal or temporary taking out of service of an underground storage tank shall be in conformance with good engineering practice. (See Appendix A.)
 The removal, abandonment in place, disposal or temporary taking out of service of an underground storage tank shall be in conformance with good engineering practice. (See Appendix A.)
The removal, abandonment in place, disposal or temporary taking out of service of an underground storage tank shall be in conformance with good engineering practice. (See Appendix A.) 4.3.16.2. Aboveground Storage Tanks
1)  When an aboveground storage tank will be out of service or unsupervised for a period not exceeding 180 days, the piping from the tank shall be capped or the valves that are necessary to achieve similar isolation of the tank
shall be closed and securely locked.
When an aboveground storage tank will be out of service or unsupervised for a period not exceeding 180 days, the piping from the tank shall be capped or the valves that are necessary to achieve similar isolation of the tank
shall be closed and securely locked.
 When an aboveground storage tank will be out of service or unsupervised for a period not exceeding 180 days, the piping from the tank shall be capped or the valves that are necessary to achieve similar isolation of the tank
shall be closed and securely locked.
When an aboveground storage tank will be out of service or unsupervised for a period not exceeding 180 days, the piping from the tank shall be capped or the valves that are necessary to achieve similar isolation of the tank
shall be closed and securely locked.
2)  Where a storage tank referred to in Sentence (1) contains flammable liquids or combustible liquids, the liquid level in the tank shall be measured and compared with subsequent readings taken at intervals
not greater than one month.
Where a storage tank referred to in Sentence (1) contains flammable liquids or combustible liquids, the liquid level in the tank shall be measured and compared with subsequent readings taken at intervals
not greater than one month.
 Where a storage tank referred to in Sentence (1) contains flammable liquids or combustible liquids, the liquid level in the tank shall be measured and compared with subsequent readings taken at intervals
not greater than one month.
Where a storage tank referred to in Sentence (1) contains flammable liquids or combustible liquids, the liquid level in the tank shall be measured and compared with subsequent readings taken at intervals
not greater than one month.
3)  When an aboveground storage tank will be out of service or unsupervised for a period exceeding 180 days, all liquid and vapours shall be removed from the storage tank and its connected piping.
When an aboveground storage tank will be out of service or unsupervised for a period exceeding 180 days, all liquid and vapours shall be removed from the storage tank and its connected piping.
 When an aboveground storage tank will be out of service or unsupervised for a period exceeding 180 days, all liquid and vapours shall be removed from the storage tank and its connected piping.
When an aboveground storage tank will be out of service or unsupervised for a period exceeding 180 days, all liquid and vapours shall be removed from the storage tank and its connected piping. 4.3.16.3. Disposal
1)  Where a storage tank is to be permanently disposed of, sufficient openings shall be cut in the tank to render
it unfit for further use.
Where a storage tank is to be permanently disposed of, sufficient openings shall be cut in the tank to render
it unfit for further use.
 Where a storage tank is to be permanently disposed of, sufficient openings shall be cut in the tank to render
it unfit for further use.
Where a storage tank is to be permanently disposed of, sufficient openings shall be cut in the tank to render
it unfit for further use.
4.3.16.4.  Underground Piping Systems
Underground Piping Systems
1)  The removal, abandonment in place, disposal or temporary taking out of service of an underground piping system shall be in conformance
with good engineering practice. (See A-4.3.16.1.(1) in Appendix A.)
The removal, abandonment in place, disposal or temporary taking out of service of an underground piping system shall be in conformance
with good engineering practice. (See A-4.3.16.1.(1) in Appendix A.)
 The removal, abandonment in place, disposal or temporary taking out of service of an underground piping system shall be in conformance
with good engineering practice. (See A-4.3.16.1.(1) in Appendix A.)
The removal, abandonment in place, disposal or temporary taking out of service of an underground piping system shall be in conformance
with good engineering practice. (See A-4.3.16.1.(1) in Appendix A.)
